Although Git is a very powerful tool, I think most people would agree when I say it can also be… a total nightmare 😐 I’ve always found it very useful to visualize in my head what’s happening when working with Git: how are the branches interacting when I perform a certain command, and how will it affect the history? Why did my coworker cry when I did a hard reset on master, force pushed to origin and rimraf‘d the .git folder?
尽管 Git 是一个非常强力的工具,但如果我说这也可能是一场噩梦 ,我想大多数人也会同意.在使用 Git 的时候,我发现在我的大脑中想象发生了什么是非常有用的:在我执行特定命令的时候,分支之间是如何相互影响的,以及它会如何影响历史日志?当我在 master 分支做了硬重置(hard reset),强制推送(force push)到 master 分支并且 rimraf .git 目录之后,我的同事为什么会哭?
I thought it would be the perfect use case to create some visualized examples of the most common and useful commands! 🥳 Many of the commands I’m covering have optional arguments that you can use in order to change their behavior. In my examples, I’ll cover the default behavior of the commands without adding (too many) config options! 😄
我认为为最常用和最有用的命令创建一些可视化的图例将会成为完美的使用示例! 我涉及到的许多命令拥有可选的参数,您可以使用这些参数来更改命令的行为.在示例中,我将会涉及没有添加(太多)配置项命令的默认行为!
Merging
Having multiple branches is extremely convenient to keep new changes separated from each other, and to make sure you don’t accidentally push unapproved or broken changes to production. Once the changes have been approved, we want to get these changes in our production branch!
拥有多个分支是很方便的,这样可以将不同的新修改互相隔离开,而且还能确保你不会意外地向生产代码推送未经许可或破损的代码修改.但一旦这些修改得到了批准许可,我们就需要将其部署到我们的生产分支中!
One way to get the changes from one branch to another is by performing a git merge! There are two types of merges Git can perform: a fast-forward, or a no-fast-forward 🐢
可将一个分支的修改融入到另一个分支的一种方式是执行
git merge.Git 可执行两种类型的合并:fast-forward 和 no-fast-forward.
This may not make a lot of sense right now, so let’s look at the differences!
现在你可能分不清,但我们马上就来看看它们的差异所在.
Fast-forward (--ff)
A fast-forward merge can happen when the current branch has no extra commits compared to the branch we’re merging. Git is… lazy and will first try to perform the easiest option: the fast-forward! This type of merge doesn’t create a new commit, but rather merges the commit(s) on the branch we’re merging right in the current branch 🥳
在当前分支相比于我们要合并的分支没有额外的提交时,可以执行
fast-forward合并.Git 很懒,首先会尝试执行最简单的选项:fast-forward!这类合并不会创建新的提交,而是会将我们正在合并的分支上的提交直接合并到当前分支.
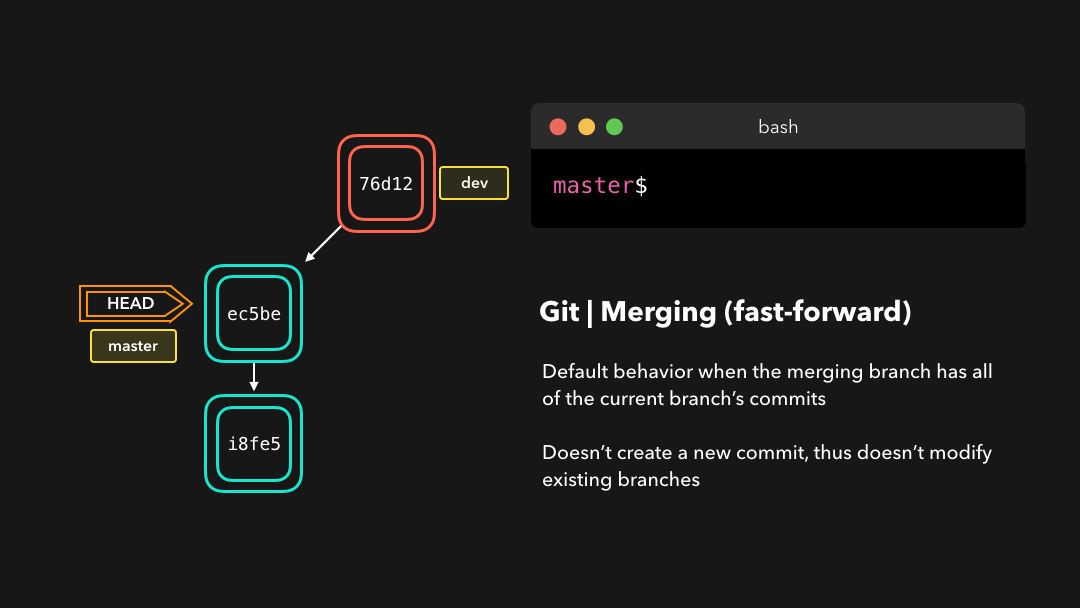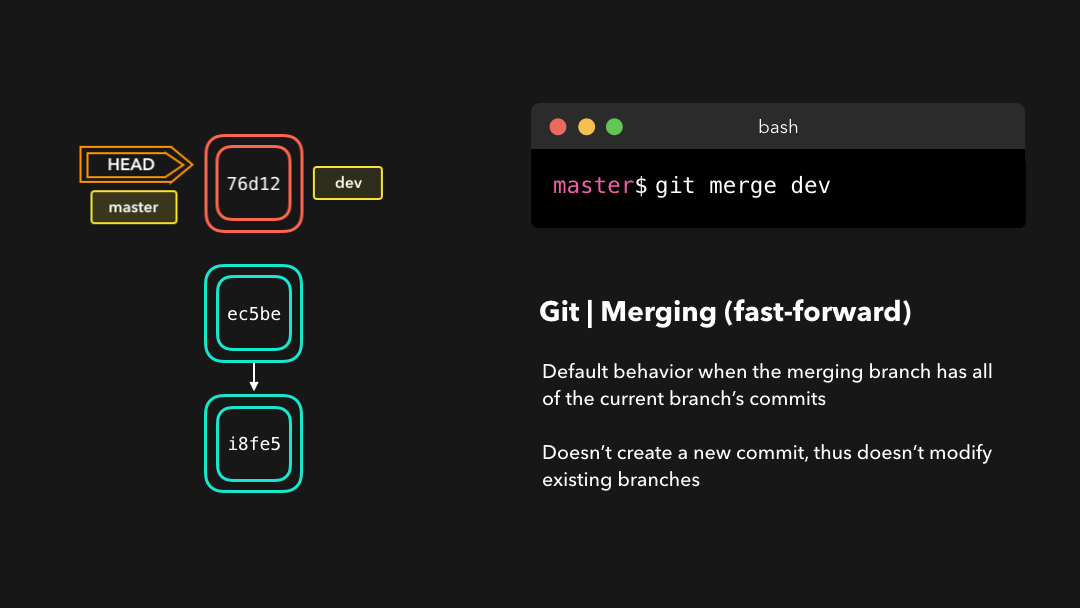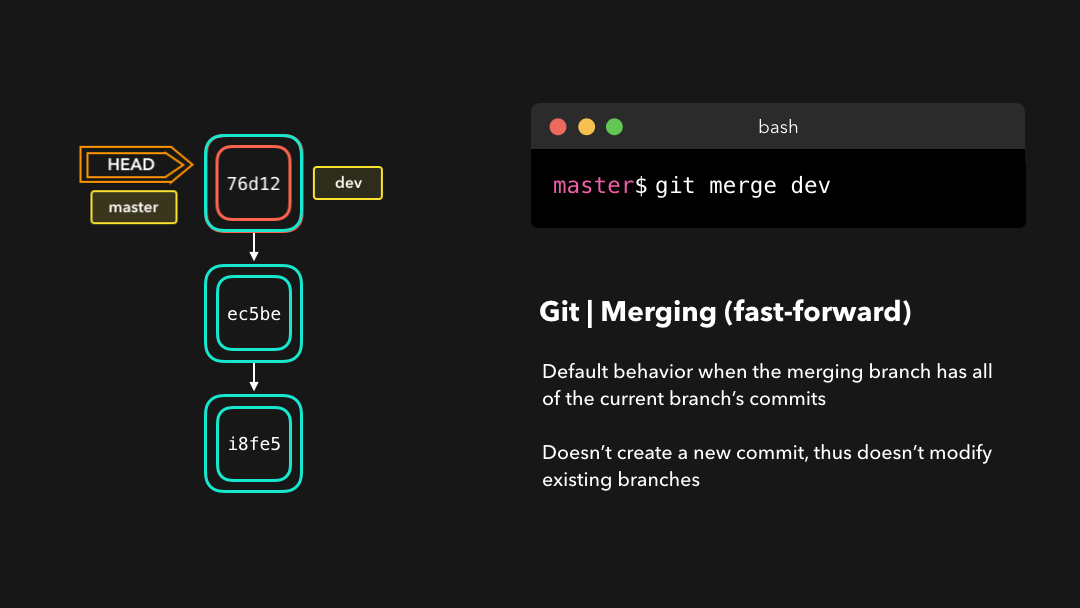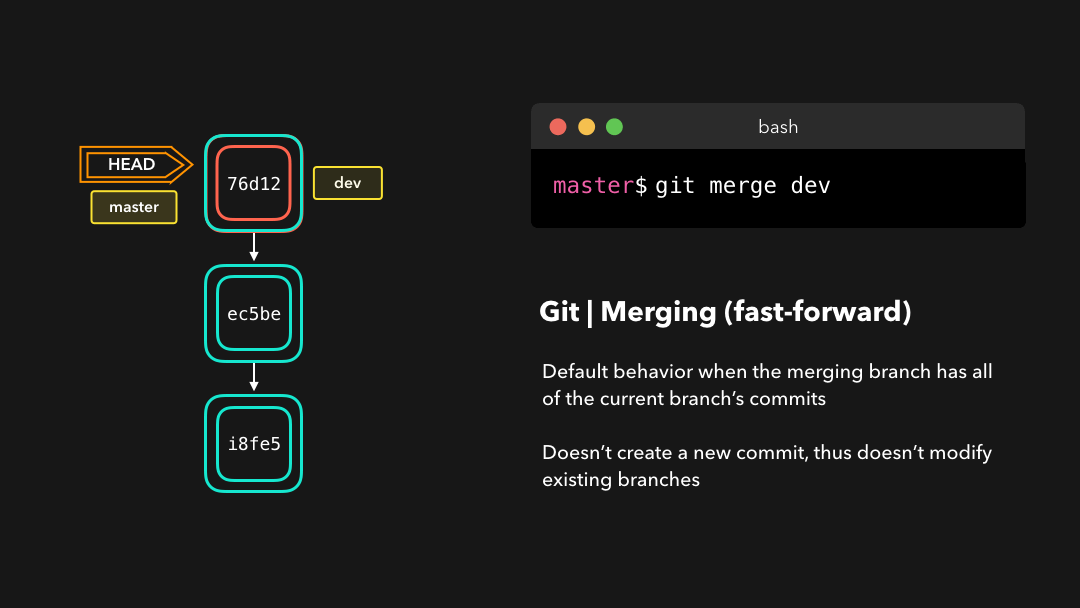
Perfect! We now have all the changes that were made on the dev branch available on the master branch. So, what’s the no-fast-forward all about?
完美!现在,我们在
dev分支上所做的所有改变都合并到了master分支上.那么 no-fast-forward 又是什么意思呢?
No-fast-foward (--no-ff)
It’s great if your current branch doesn’t have any extra commits compared to the branch that you want to merge, but unfortunately that’s rarely the case! If we committed changes on the current branch that the branch we want to merge doesn’t have, git will perform a no-fast-forward merge.
如果你的当前分支相比于你想要合并的分支没有任何提交,那当然很好,但很遗憾现实情况很少如此!如果我们在当前分支上提交我们想要合并的分支不具备的改变,那么 git 将会执行 no-fast-forward 合并.
With a no-fast-forward merge, Git creates a new merging commit on the active branch. The commit’s parent commits point to both the active branch and the branch that we want to merge!
使用 no-fast-forward 合并时,Git 会在当前活动分支上创建新的 merging commit .这个提交的父提交既指向这个活动分支,也指向我们想要合并的分支!
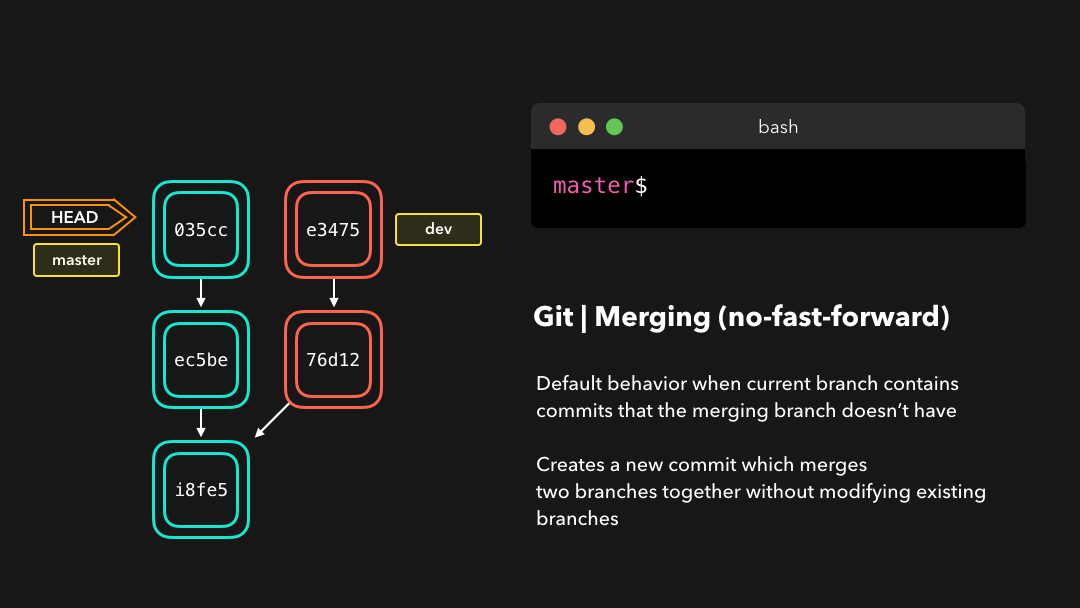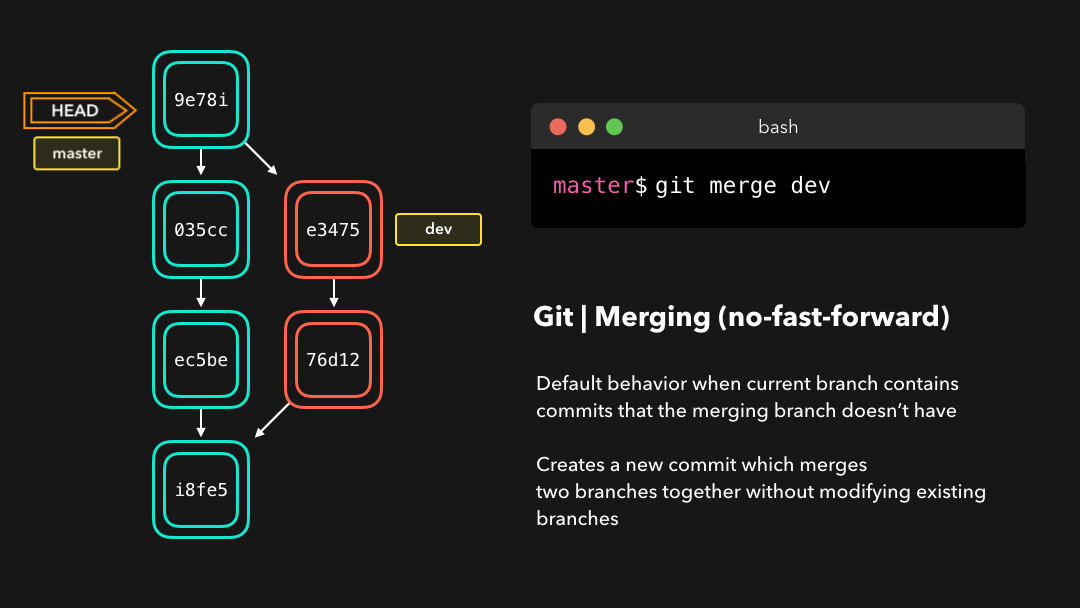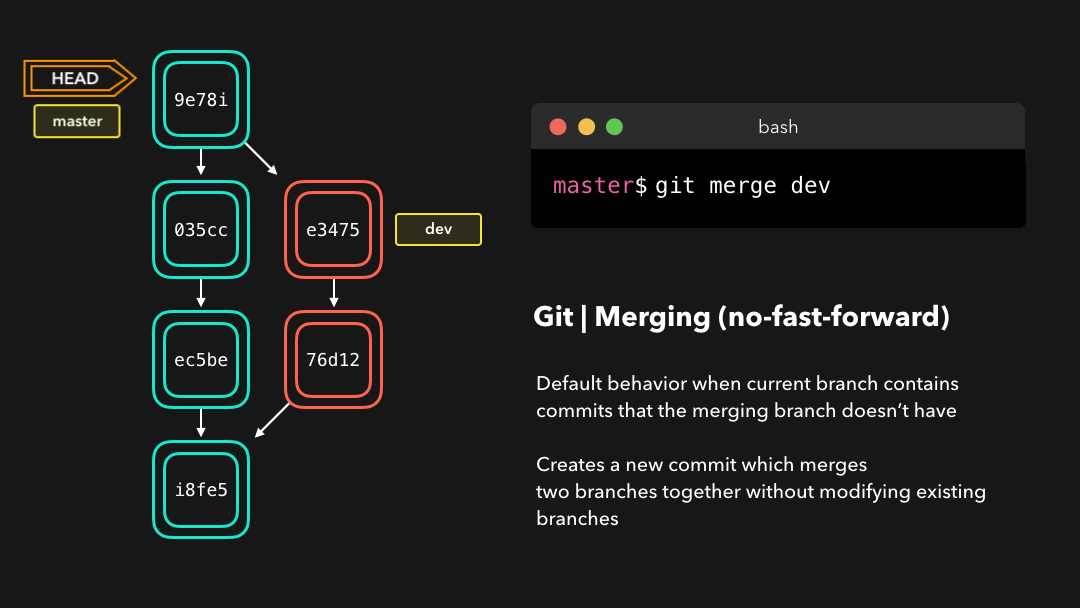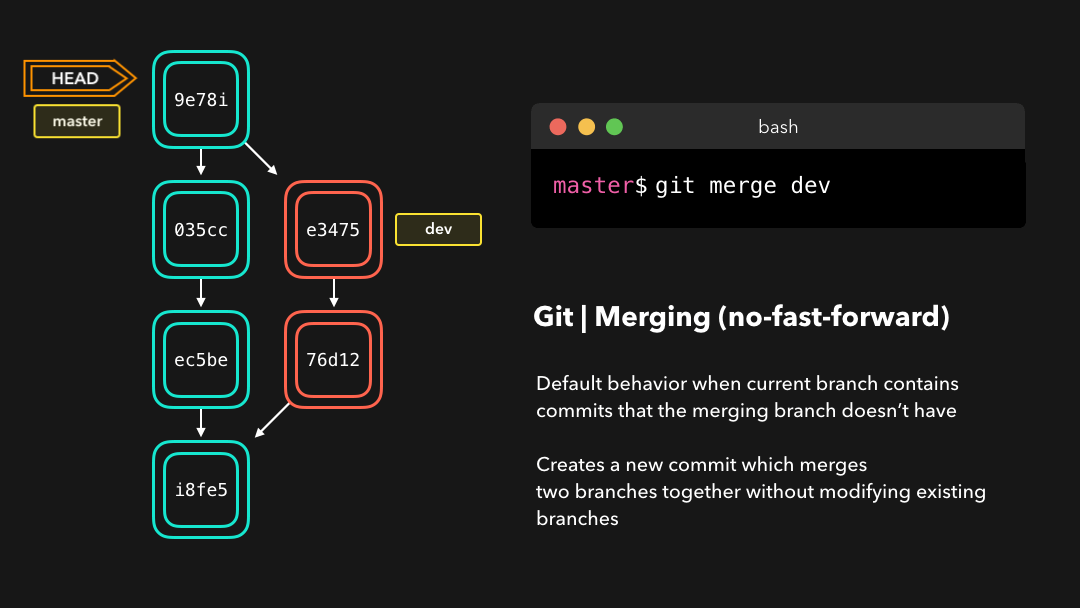
No big deal, a perfect merge! 🎉 The master branch now contains all the changes that we’ve made on the dev branch.
没什么大不了的,完美的合并!现在,
我们在dev分支上所做的所有改变都合并到了master分支上.master分支包含我们在dev分支上所做的所有改变.
Merge Conflicts
Although Git is good at deciding how to merge branches and add changes to files, it cannot always make this decision all by itself 🙂 This can happen when the two branches we’re trying to merge have changes on the same line in the same file, or if one branch deleted a file that another branch modified, and so on.
尽管 Git 能够很好地决定如何合并分支以及如何向文件添加修改,但它并不总是能完全自己做决定.当我们想要合并的两个分支的同一文件中的同一行代码上有不同的修改,或者一个分支删除了一个文件而另一个分支修改了这个文件时,Git 就不知道如何取舍了.
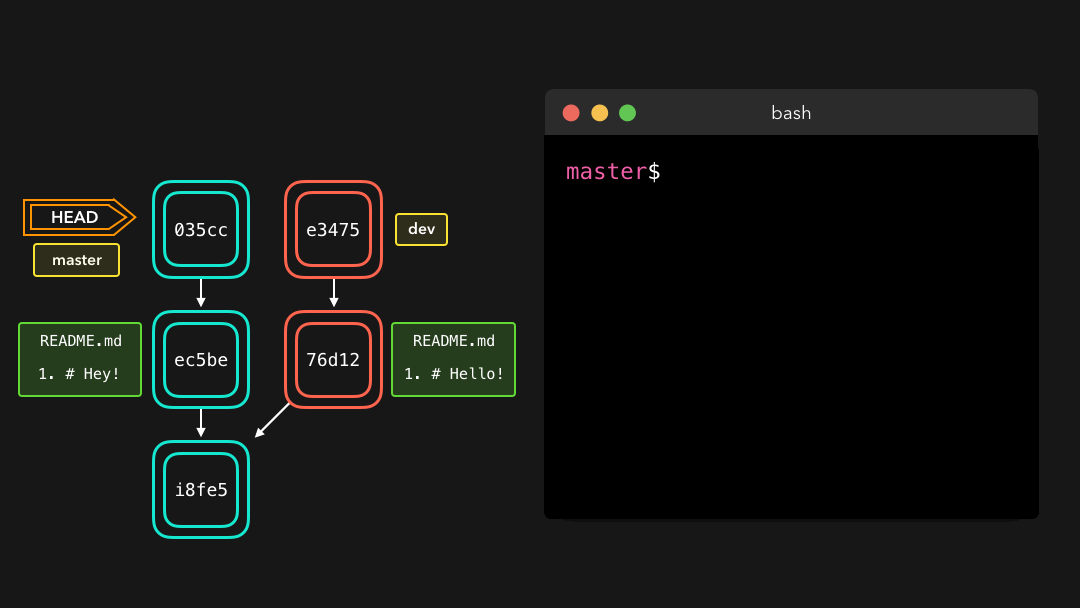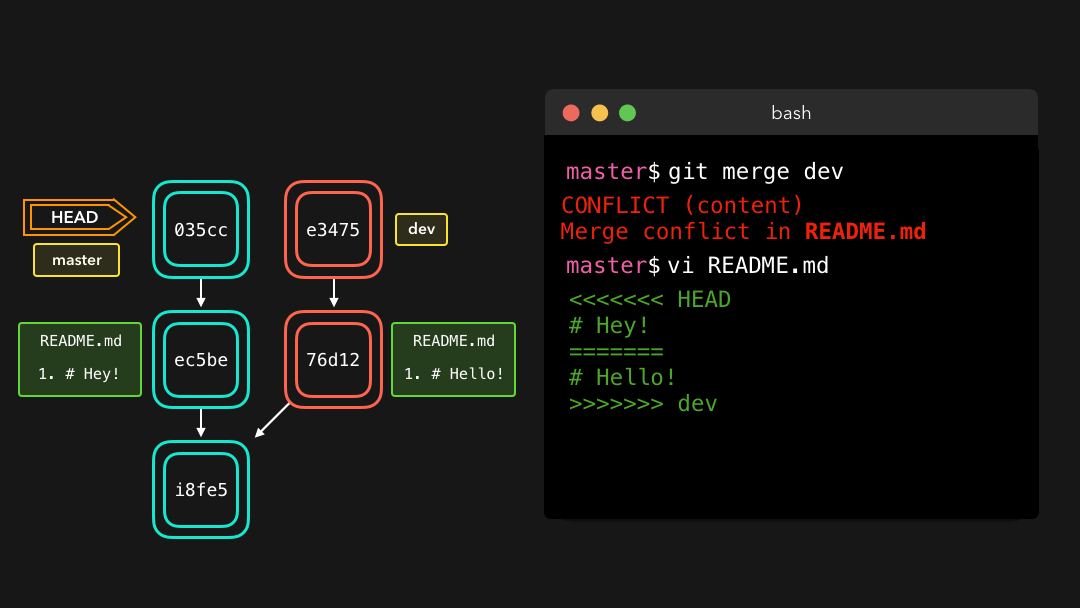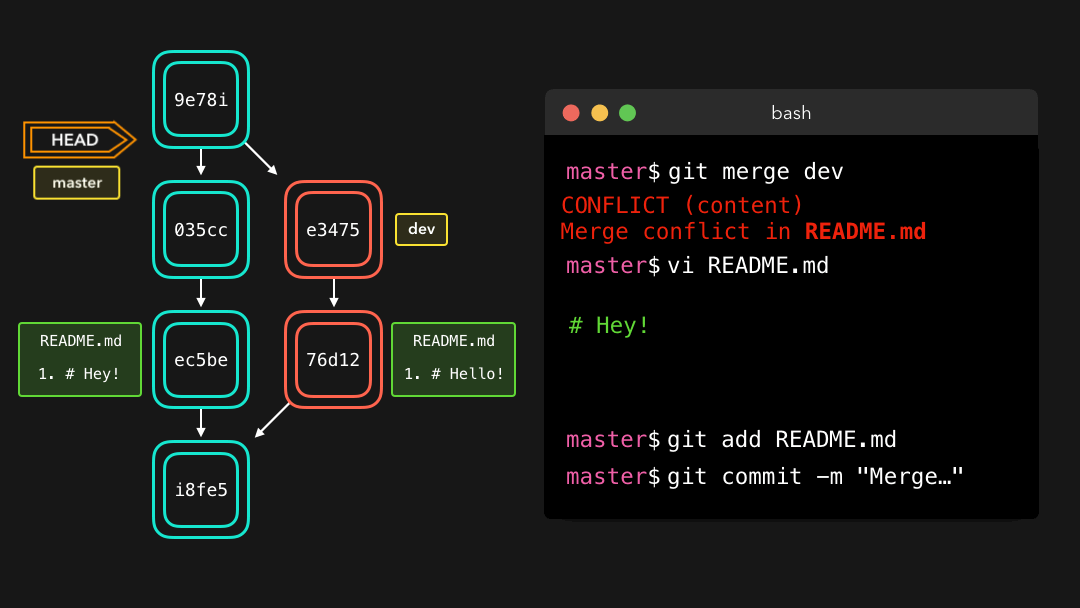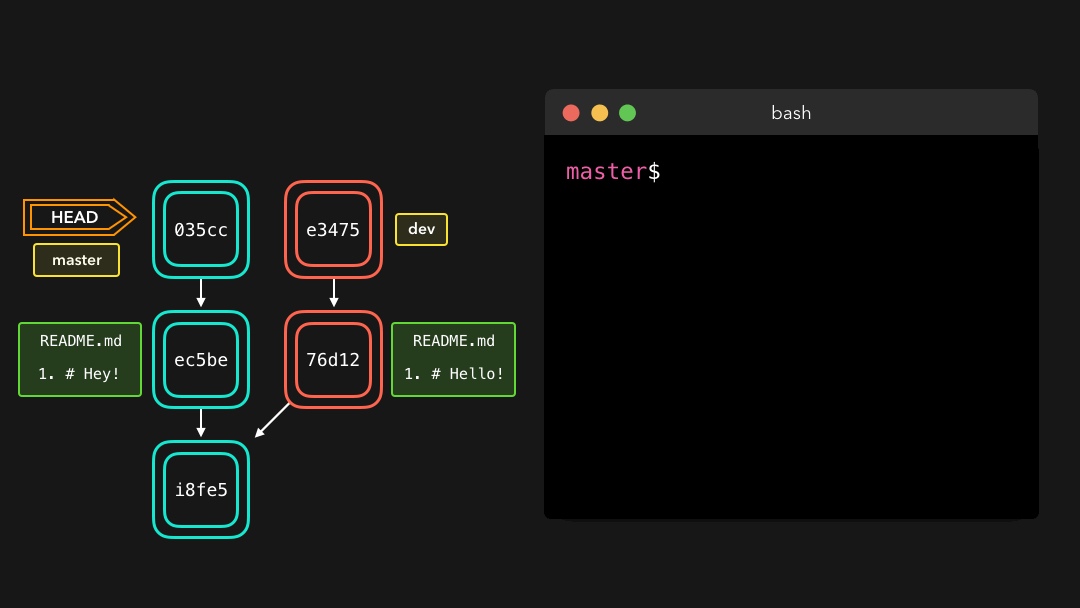
In that case, Git will ask you to help decide which of the two options we want to keep! Let’s say that on both branches, we edited the first line in the README.md.
在这样的情况下,Git 会询问你想要保留哪种选择?假设在这两个分支中,我们都编辑了 README.md 的第一行.
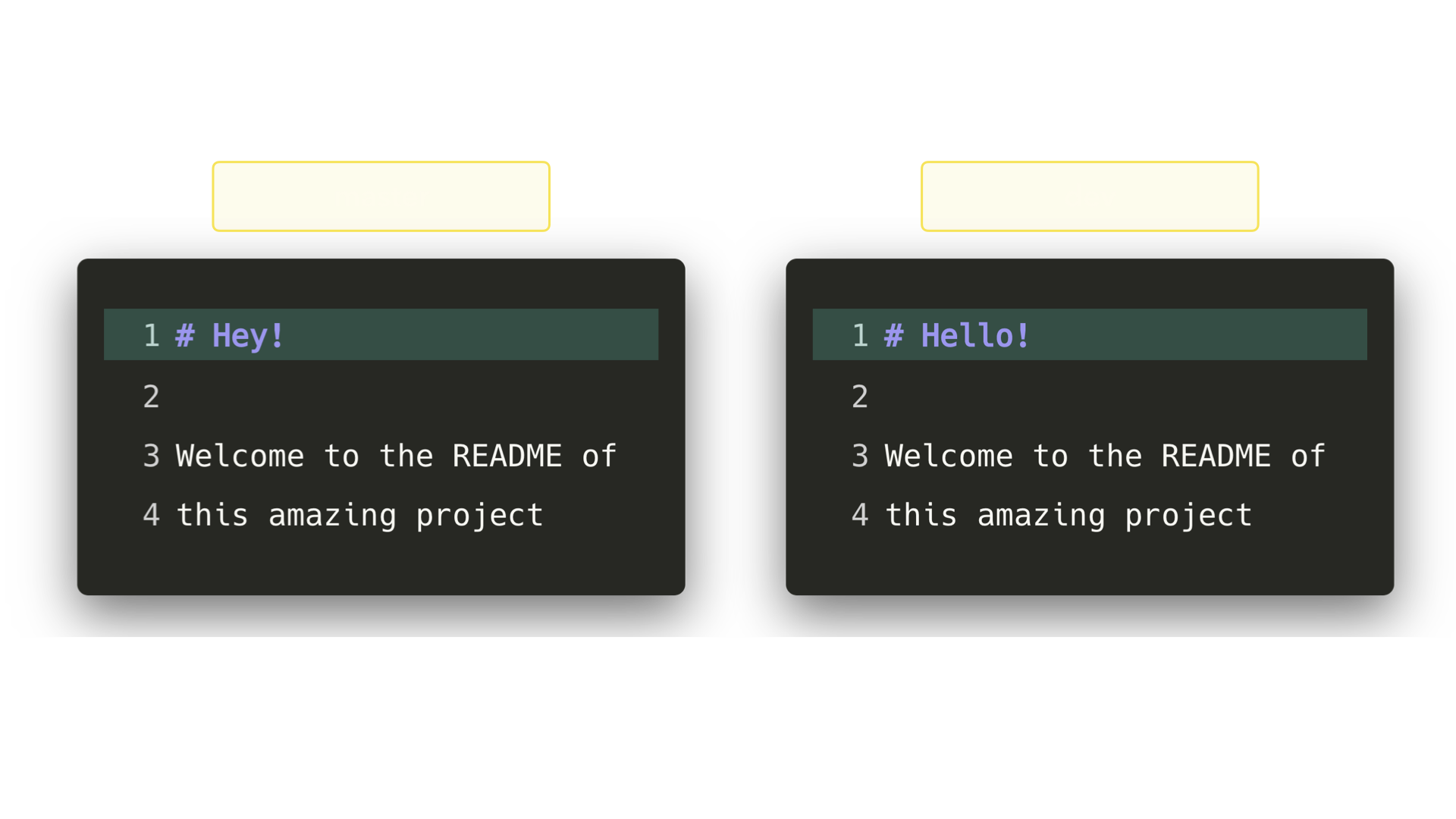
If we want to merge dev into master, this will end up in a merge conflict: would you like the title to be Hello! or Hey!?
如果我们想把 dev 合并到 master,就会出现一个合并冲突:你想要标题是 Hello! 还是 Hey!?
When trying to merge the branches, Git will show you where the conflict happens. We can manually remove the changes we don’t want to keep, save the changes, add the changed file again, and commit the changes 🥳
当尝试合并这些分支时,Git 会向你展示冲突出现的位置.我们可以手动移除我们不想保留的修改,保存这些修改,再次添加这个已修改的文件,然后提交这些修改.
Yay! Although merge conflicts are often quite annoying, it makes total sense: Git shouldn’t just assume which change we want to keep.
完成!尽管合并冲突往往很让人厌烦,但这是合理的:Git 不应该瞎猜我们想要保留哪些修改.
Rebasing
We just saw how we could apply changes from one branch to another by performing a git merge. Another way of adding changes from one branch to another is by performing a git rebase.
我们刚看到可通过执行
git merge将一个分支的修改应用到另一个分支.另一种可将一个分支的修改融入到另一个分支的方式是执行git rebase.
A git rebase copies the commits from the current branch, and puts these copied commits on top of the specified branch.
git rebase会将当前分支的提交复制到指定的分支之上.
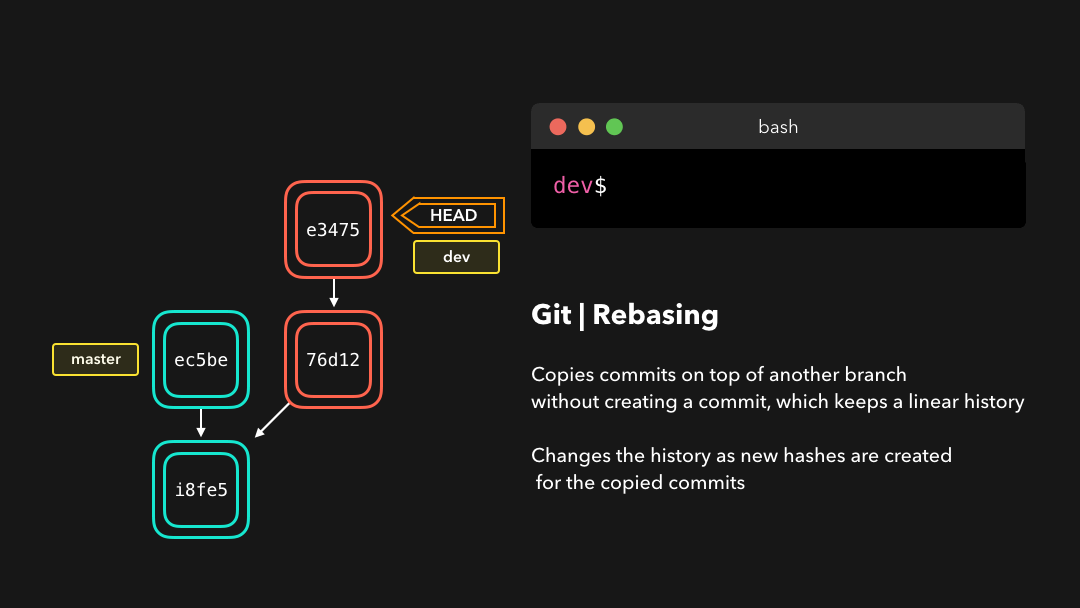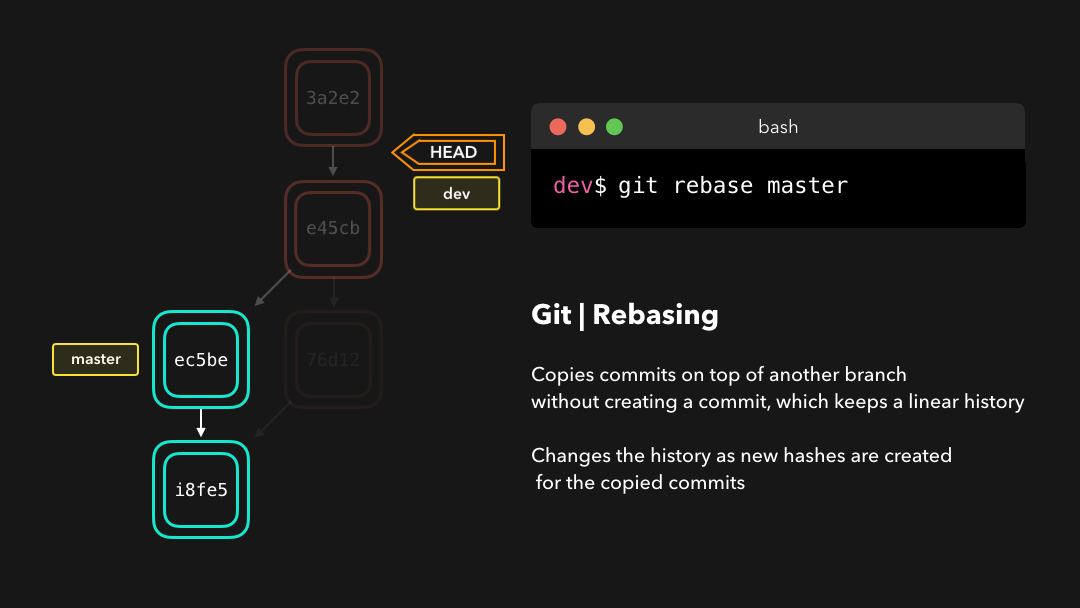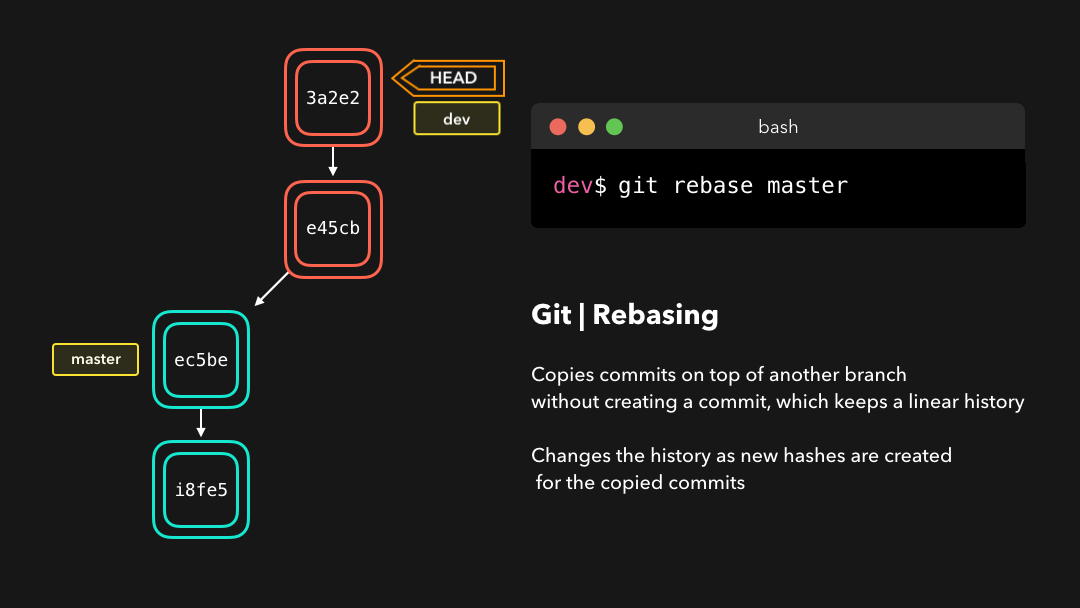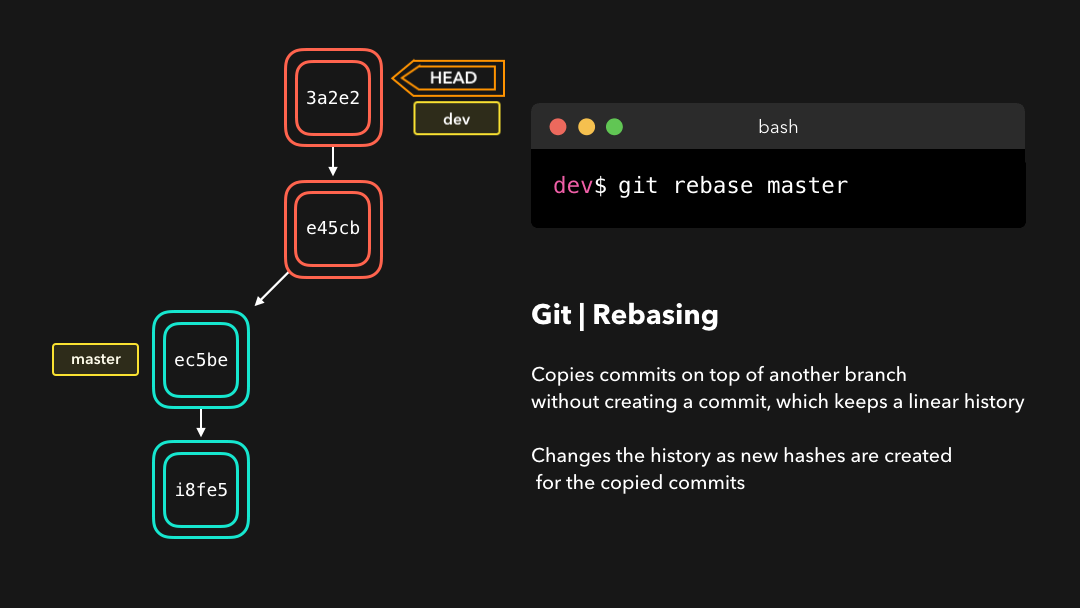
Perfect, we now have all the changes that were made on the master branch available on the dev branch! 🎊
完美,现在我们在
dev分支上获取了master分支上的所有修改.
A big difference compared to merging, is that Git won’t try to find out which files to keep and not keep. The branch that we’re rebasing always has the latest changes that we want to keep! You won’t run into any merging conflicts this way, and keeps a nice linear Git history.
变基与合并有一个重大的区别:Git 不会尝试确定要保留或不保留哪些文件.我们执行 rebase 的分支总是含有我们想要保留的最新近的修改!这样我们不会遇到任何合并冲突,而且可以保留一个漂亮的、线性的 Git 历史记录.
This example shows rebasing on the master branch. In bigger projects, however, you usually don’t want to do that. A git rebase changes the history of the project as new hashes are created for the copied commits!
上面这个例子展示了在
master分支上的变基.但是,在更大型的项目中,你通常不需要这样的操作.git rebase在为复制的提交创建新的 hash 时会修改项目的历史记录.
Rebasing is great whenever you’re working on a feature branch, and the master branch has been updated. You can get all the updates on your branch, which would prevent future merging conflicts! 😄
如果你在开发一个 feature 分支并且 master 分支已经更新过,那么变基就很好用.你可以在你的分支上获取所有更新,这能防止未来出现合并冲突.
Interactive Rebase
Before rebasing the commits, we can modify them! 😃 We can do so with an interactive rebase. An interactive rebase can also be useful on the branch you’re currently working on, and want to modify some commits.
在为提交执行变基之前,我们可以修改它们!我们可以使用 交互式变基 来完成这一任务.交互式变基在你当前开发的分支上以及想要修改某些提交时会很有用.
There are 6 actions we can perform on the commits we’re rebasing:
在我们正在 rebase 的提交上,我们可以执行以下 6 个动作:
reword: Change the commit message(reword:修改提交信息;)edit: Amend this commit(edit:修改此提交;)squash: Meld commit into the previous commit(squash:将提交融合到前一个提交中;)fixup: Meld commit into the previous commit, without keeping the commit’s log message(fixup:将提交融合到前一个提交中,不保留该提交的日志消息;)exec: Run a command on each commit we want to rebase(exec:在每个提交上运行我们想要 rebase 的命令;)drop: Remove the commit(drop:移除该提交.)
Awesome! This way, we can have full control over our commits. If we want to remove a commit, we can just drop it.
很棒!这样我们就能完全控制我们的提交了.如果你想要移除一个提交,只需
drop即可.
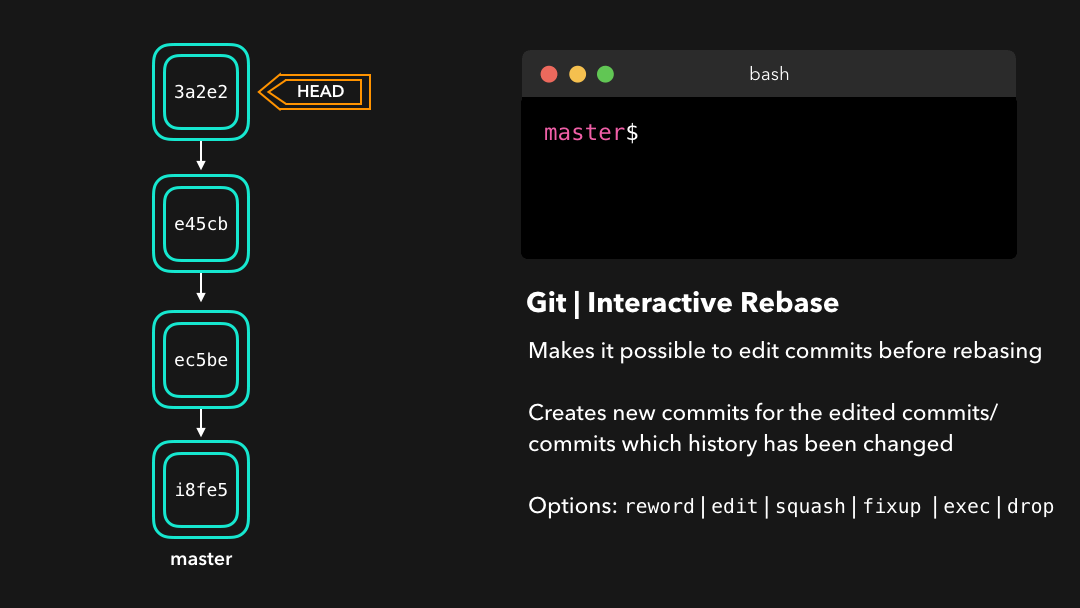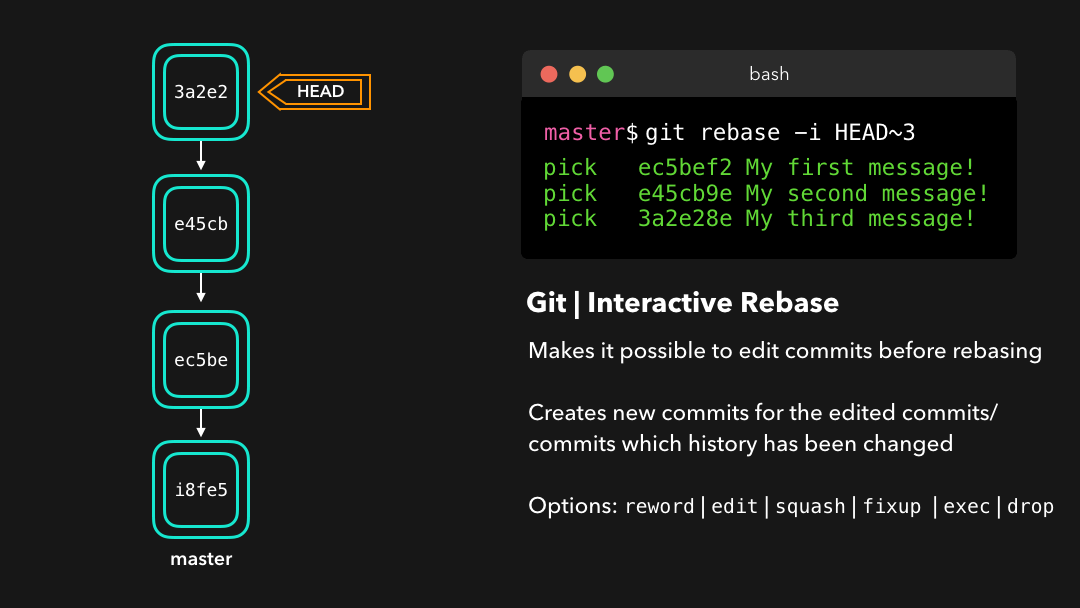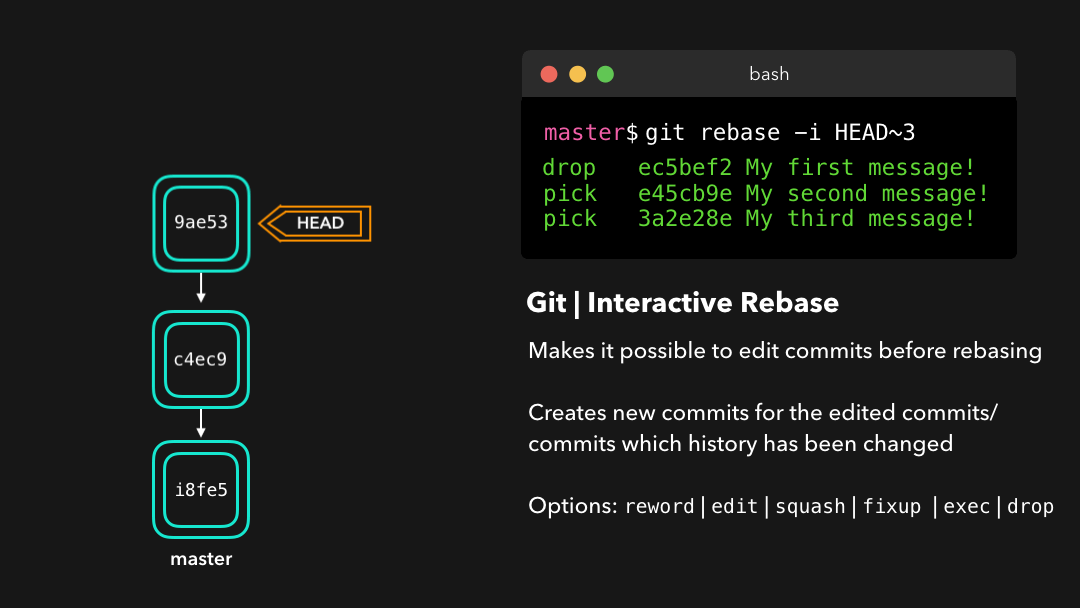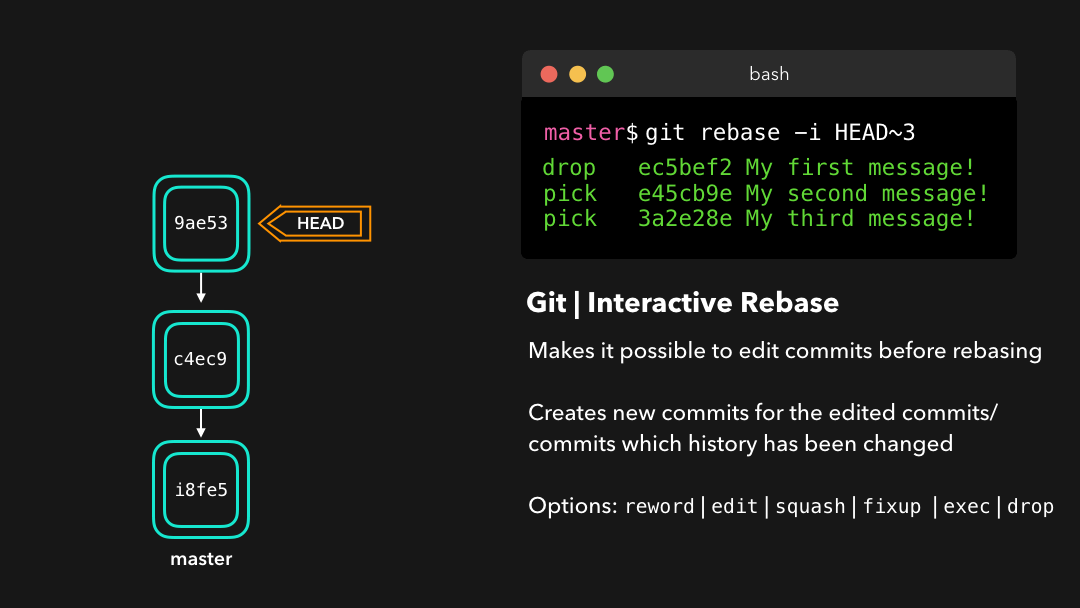
Or if we want to squash multiple commits together to get a cleaner history, no problem!
如果你想把多个提交融合到一起以便得到清晰的提交历史,那也没有问题!
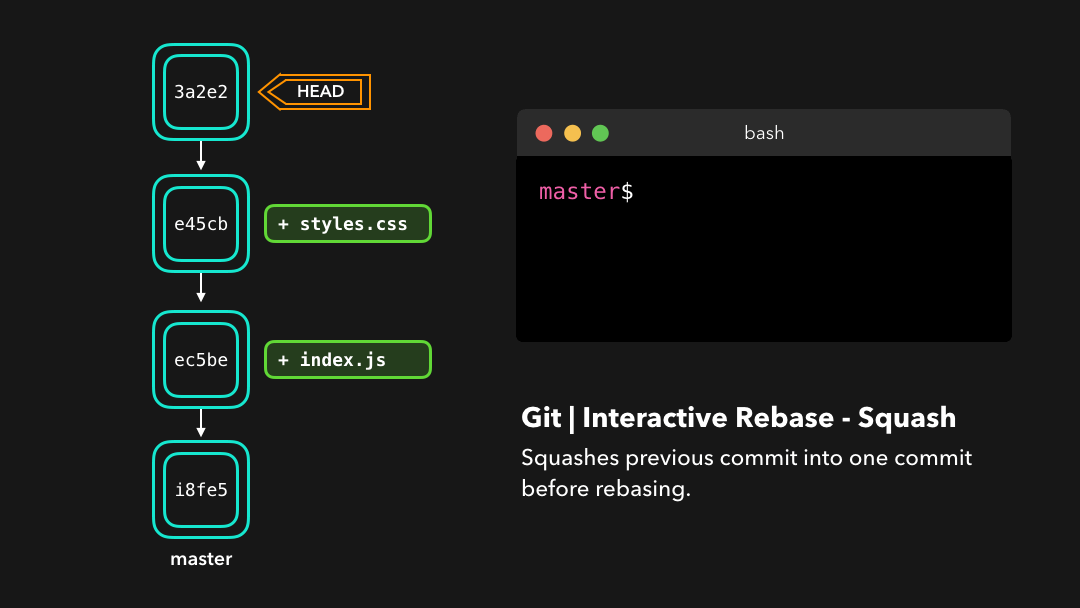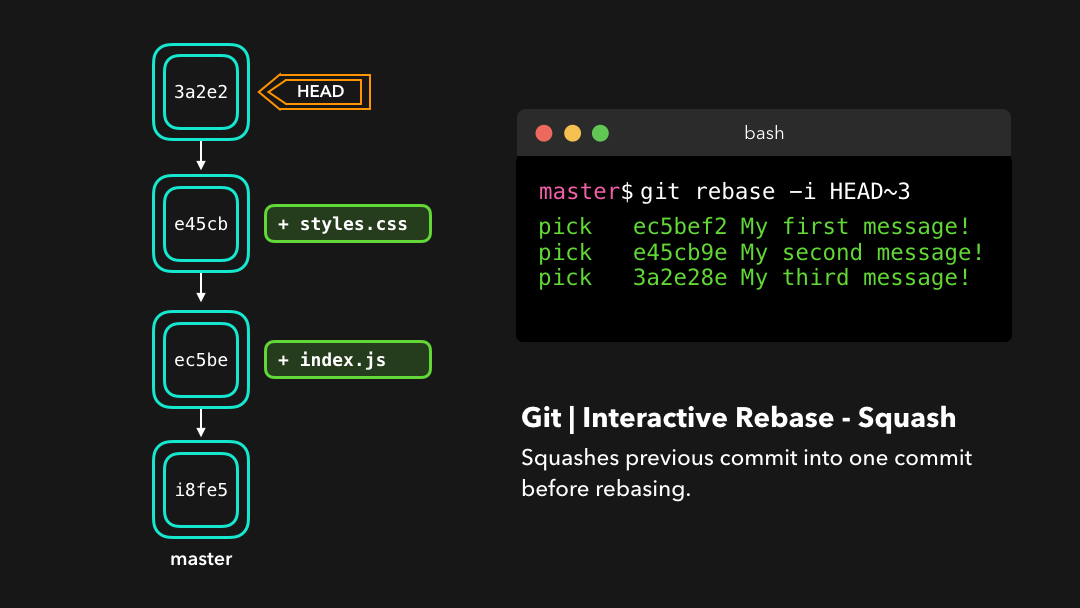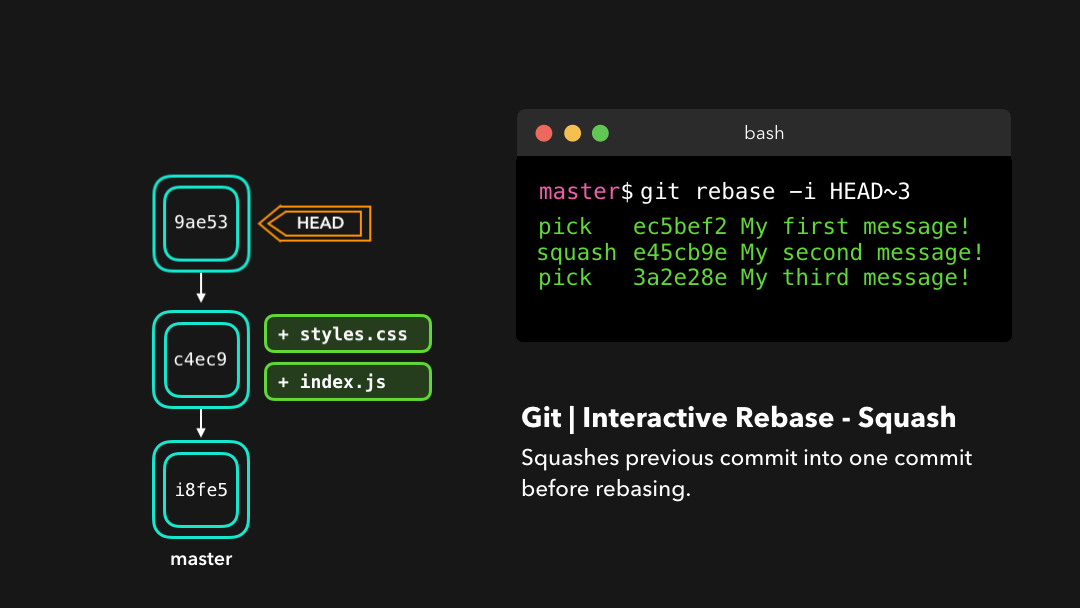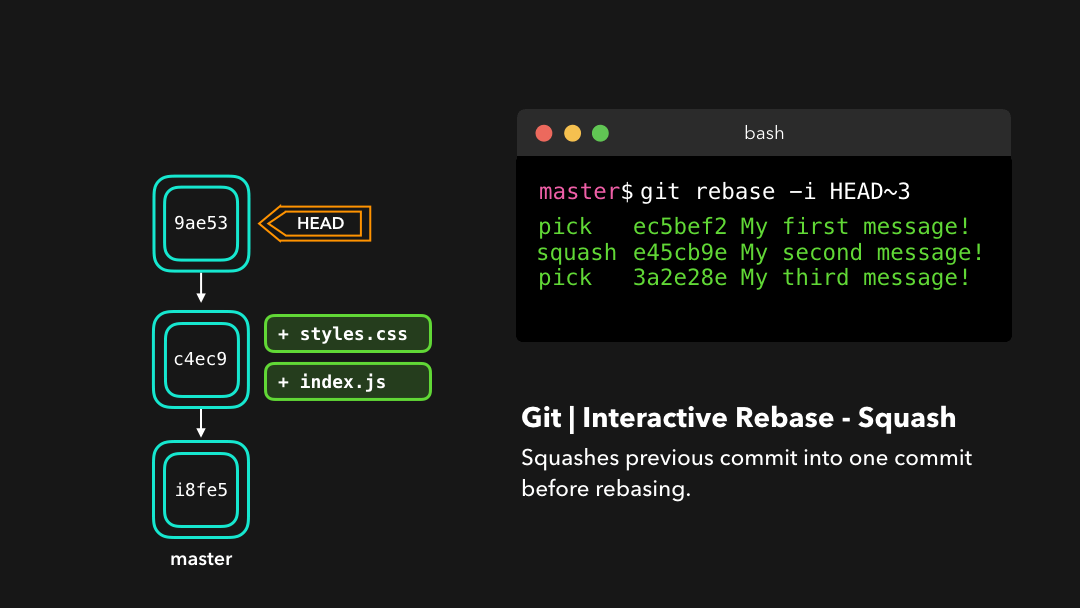
Interactive rebasing gives you a lot of control over the commits you’re trying to rebase, even on the current active branch!
交互式变基能为你在 rebase 时提供大量控制,甚至可以控制当前的活动分支.
Resetting
It can happen that we committed changes that we didn’t want later on. Maybe it’s a WIP commit, or maybe a commit that introduced bugs! 🐛 In that case, we can perform a git reset.
当我们不想要之前提交的修改时,就会用到这个命令.也许这是一个
WIP提交或者可能是引入了 bug 的提交,这时候就要执行git reset.
A git reset gets rid of all the current staged files and gives us control over where HEAD should point to.
git reset能让我们不再使用当前已暂存的文件,让我们可以控制HEAD应该指向的位置.
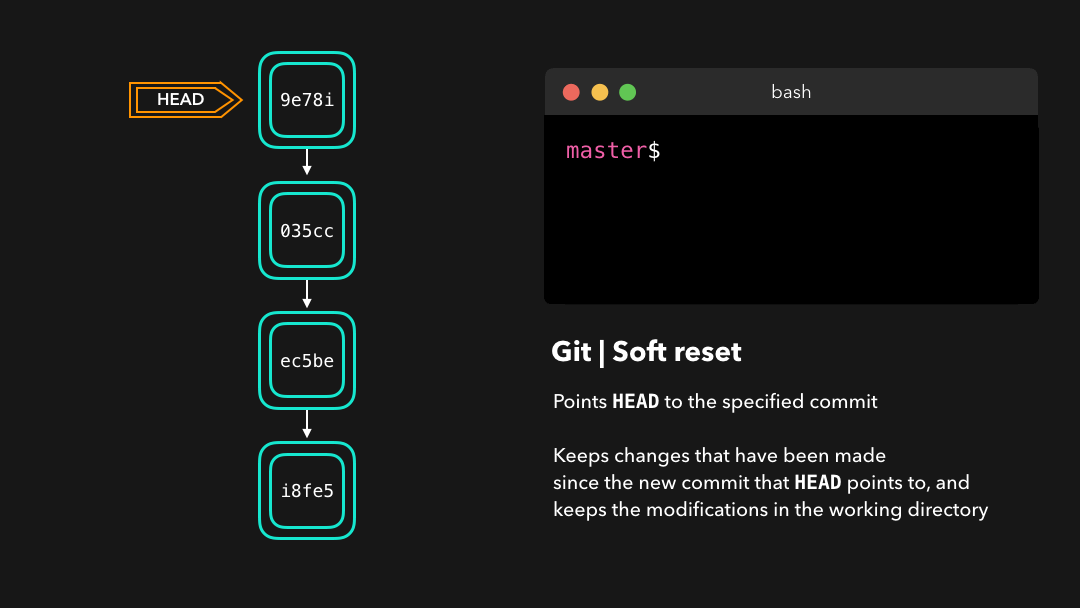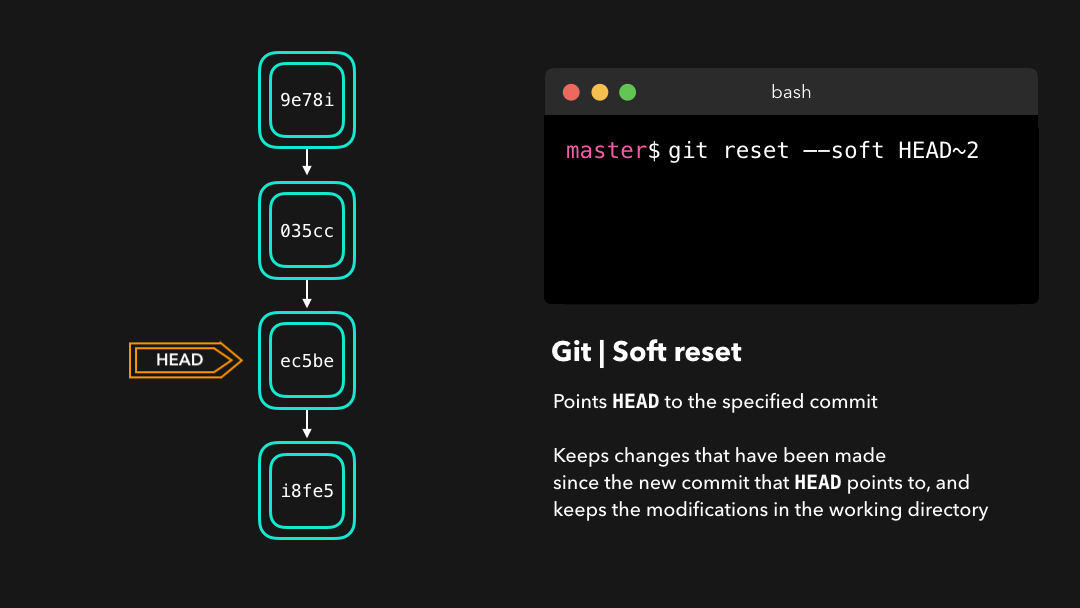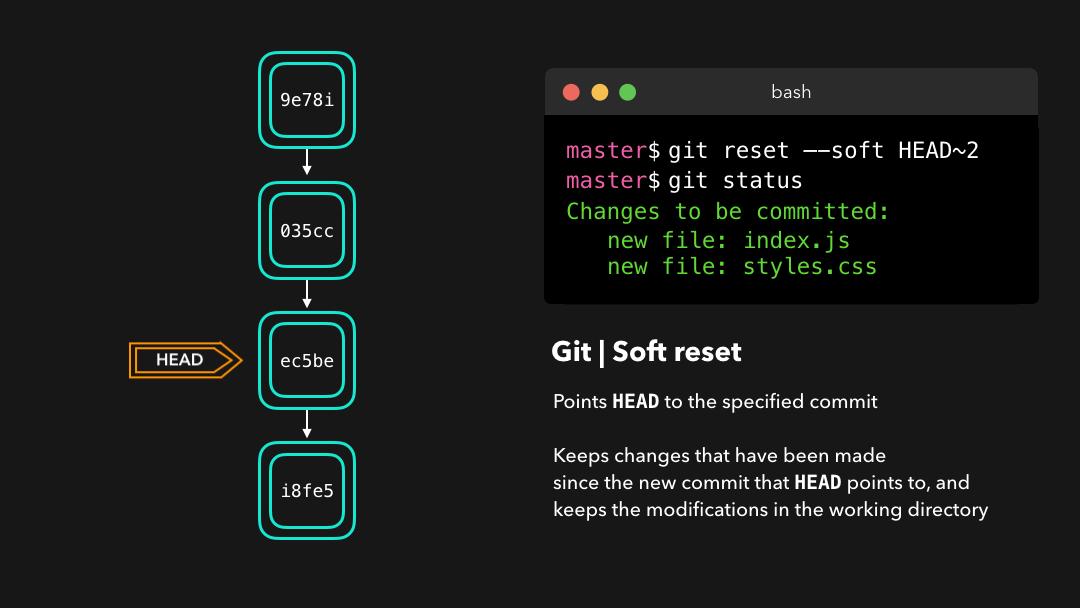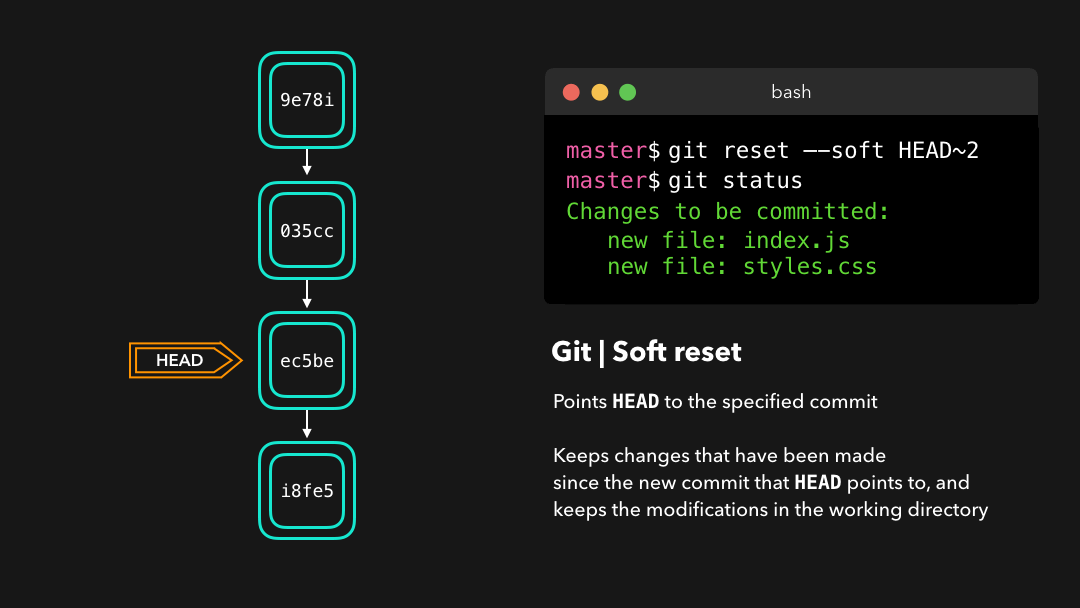
Soft reset
A soft reset moves HEAD to the specified commit (or the index of the commit compared to HEAD), without getting rid of the changes that were introduced on the commits afterward!
软重置 会将
HEAD移至指定的提交(或与HEAD相比的提交的索引),而不会移除该提交之后加入的修改!
Let’s say that we don’t want to keep the commit 9e78i which added a style.css file, and we also don’t want to keep the commit 035cc which added an index.js file. However, we do want to keep the newly added style.css and index.js file! A perfect use case for a soft reset.
假设我们不想保留添加了一个
style.css文件的提交9e78i,而且我们也不想保留添加了一个index.js文件的提交035cc.但是,我们确实又想要保留新添加的style.css和index.js文件!这是软重置的一个完美用例.
When typing git status, you’ll see that we still have access to all the changes that were made on the previous commits. This is great, as this means that we can fix the contents of these files and commit them again later on!
输入
git status后,你会看到我们仍然可以访问在之前的提交上做过的所有修改.这很好,这意味着我们可以修复这些文件的内容,之后再重新提交它们!
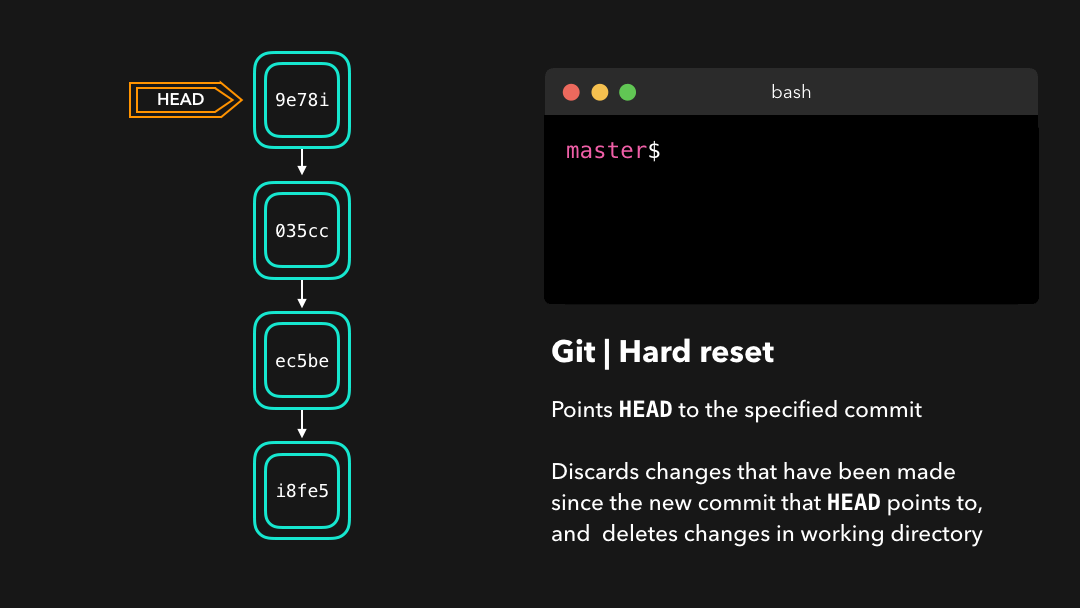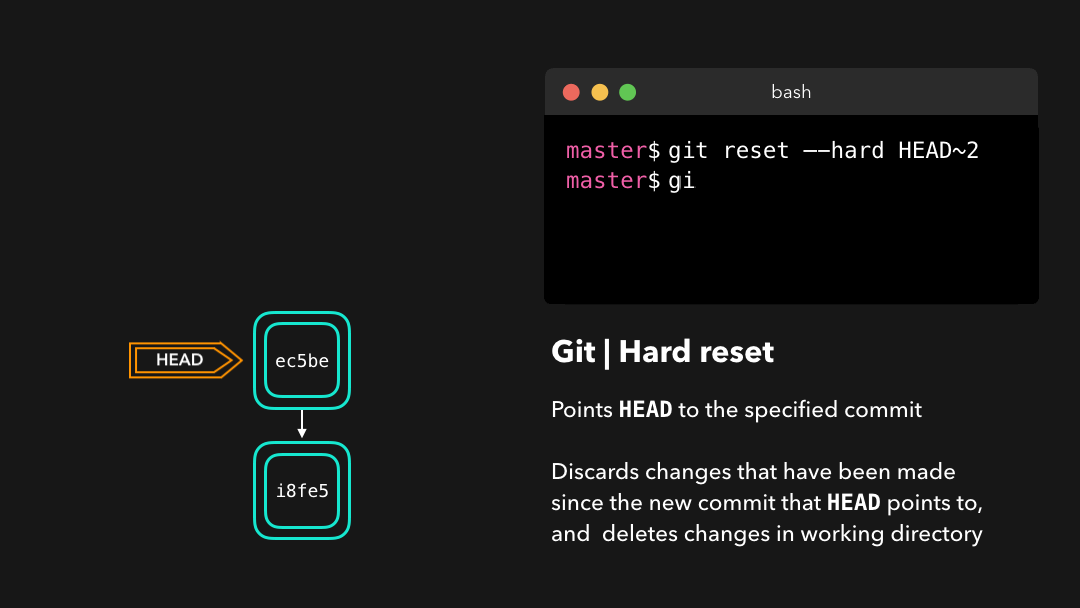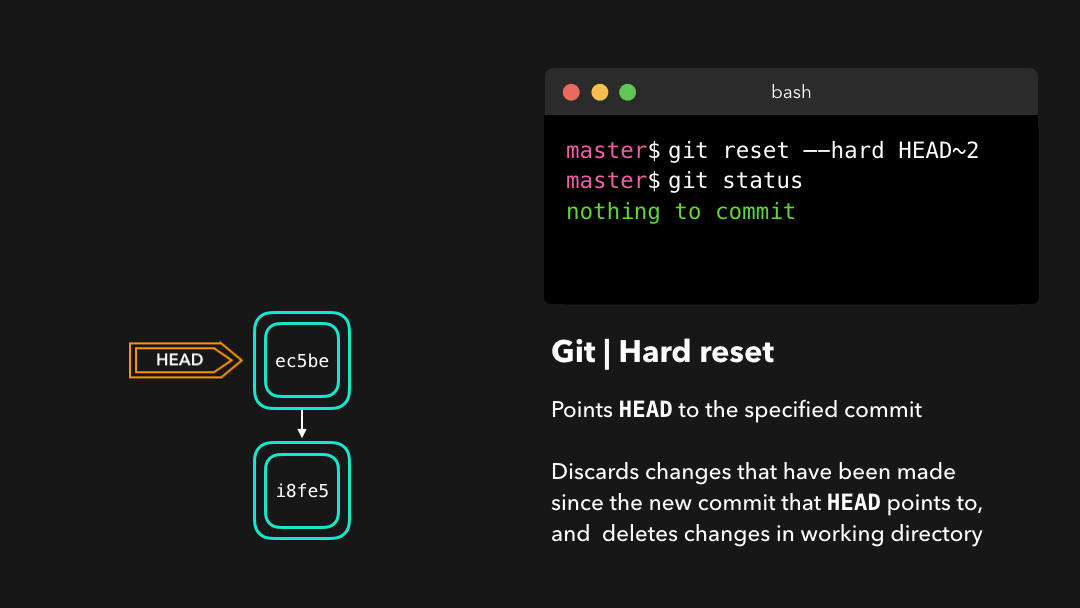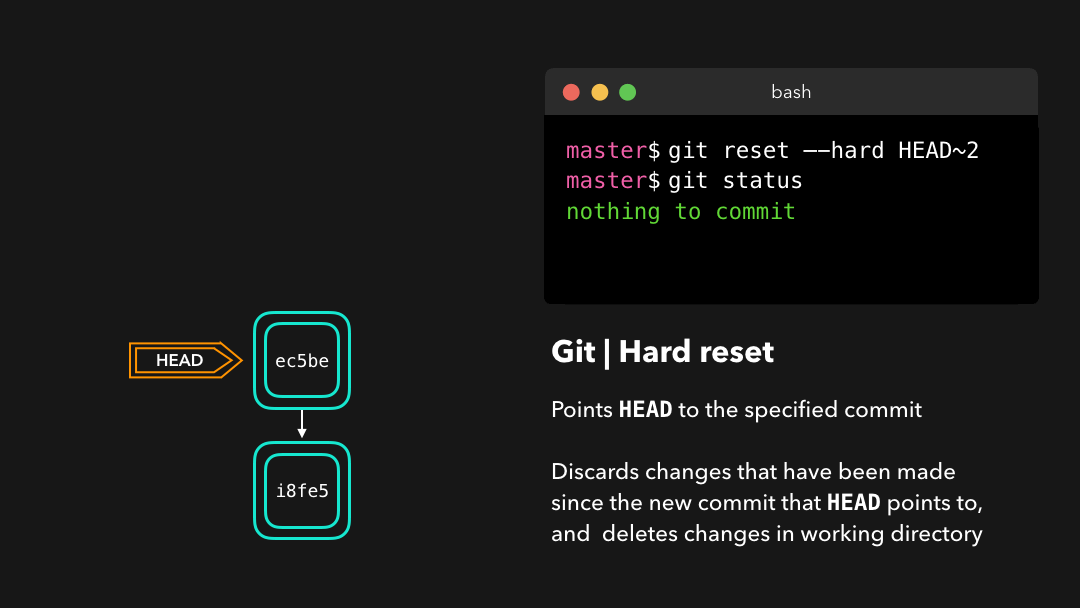
Hard reset
Sometimes, we don’t want to keep the changes that were introduced by certain commits. Unlike a soft reset, we shouldn’t need to have access to them any more. Git should simply reset its state back to where it was on the specified commit: this even includes the changes in your working directory and staged files! 💣
有时候我们并不想保留某些提交引入的修改.不同于软重置,我们应该再也无需访问它们.Git 应该直接将整体状态直接重置到特定提交之前的状态:这甚至包括你在工作目录中和已暂存文件上的修改.
Git has discarded the changes that were introduced on 9e78i and 035cc, and reset its state to where it was on commit ec5be.
Git 丢弃了
9e78i和035cc引入的修改,并将状态重置到了ec5be的状态.
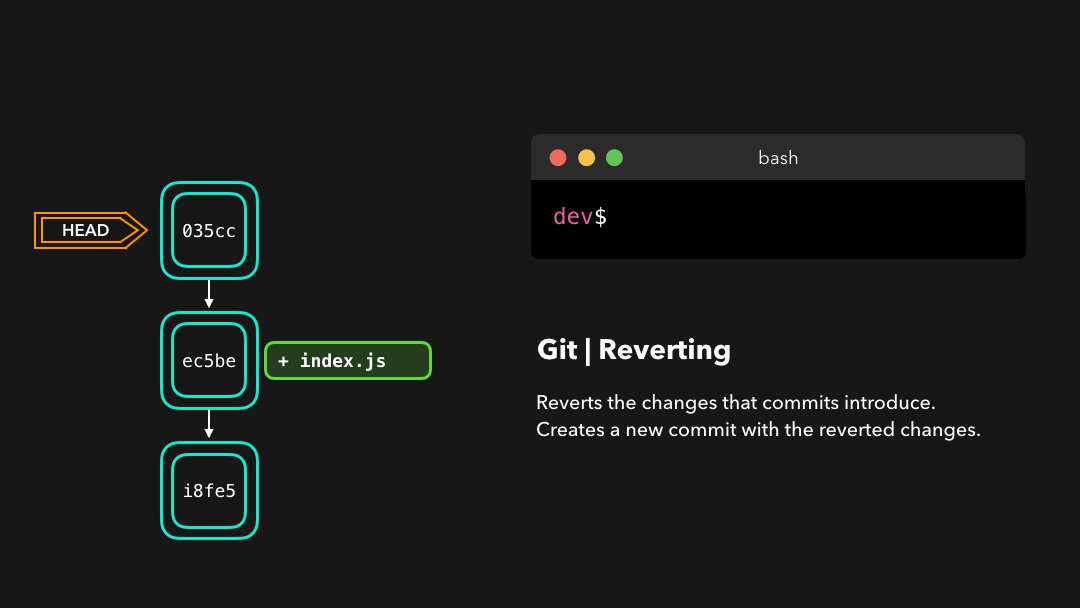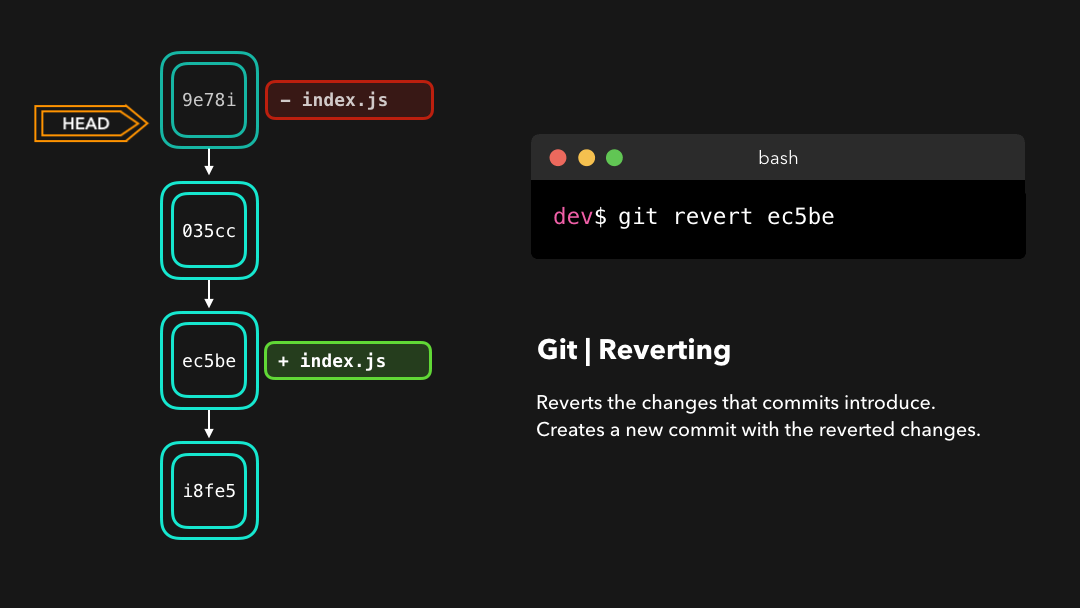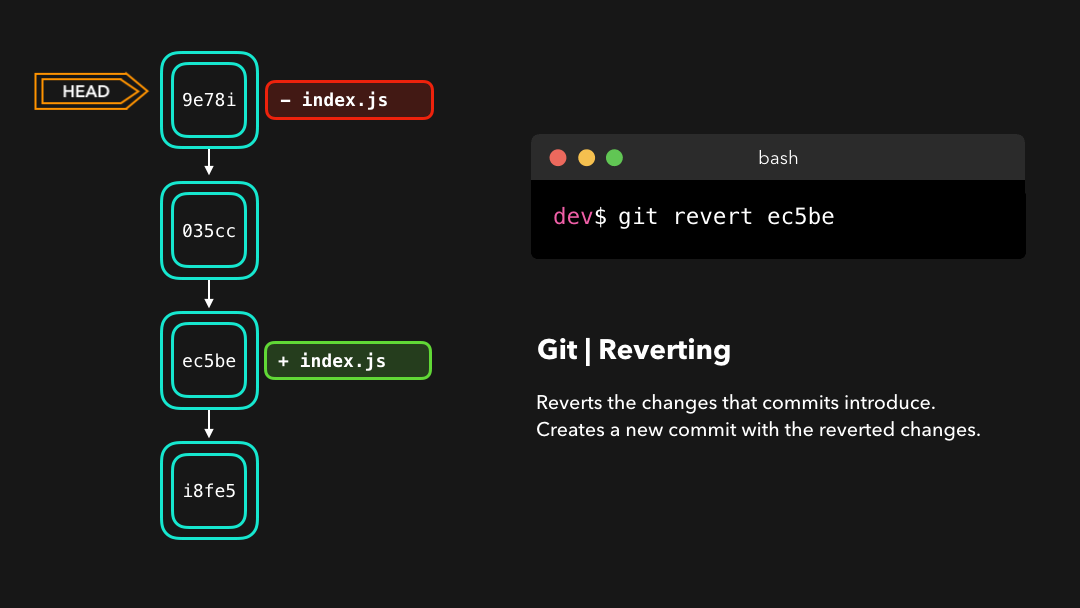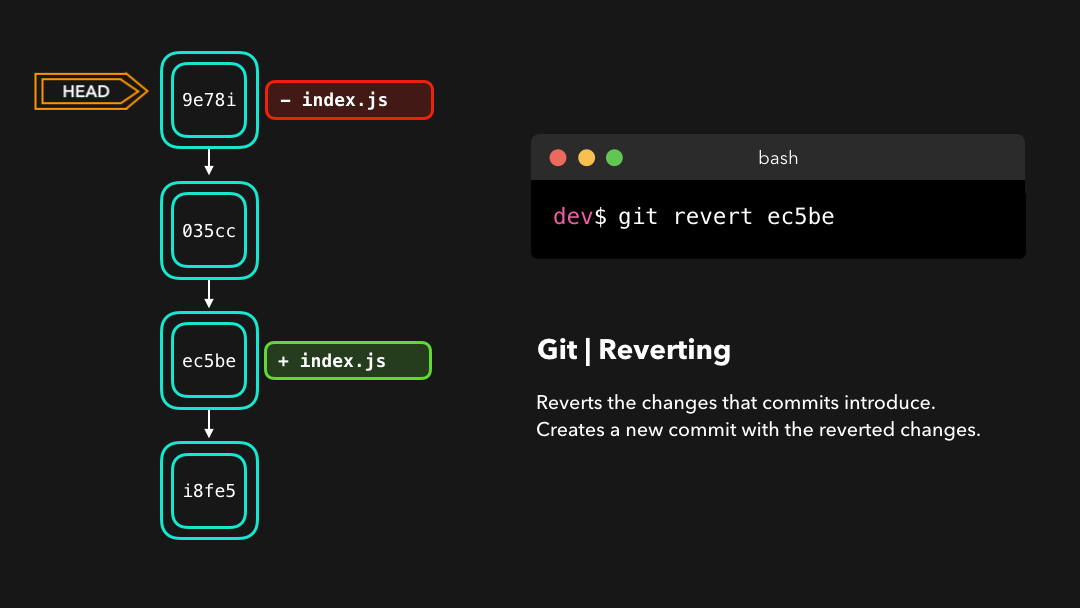
Reverting
Another way of undoing changes is by performing a git revert. By reverting a certain commit, we create a new commit that contains the reverted changes!
另一种撤销修改的方法是执行
git revert.通过对特定的提交执行还原操作,我们会创建一个包含已还原修改的 新提交.
Let’s say that ec5be added an index.js file. Later on, we actually realize we didn’t want this change introduced by this commit anymore! Let’s revert the ec5be commit.
假设
ec5be添加了一个index.js文件.但之后我们发现其实我们再也不需要由这个提交引入的修改了.那就还原ec5be提交吧!
Perfect! Commit 9e78i reverted the changes that were introduced by the ec5be commit. Performing a git revert is very useful in order to undo a certain commit, without modifying the history of the branch.
完美!提交
9e78i还原了由提交ec5be引入的修改.在撤销特定的提交时,git revert非常有用,同时也不会修改分支的历史.
Cherry-picking
When a certain branch contains a commit that introduced changes we need on our active branch, we can cherry-pick that command! By cherry-picking a commit, we create a new commit on our active branch that contains the changes that were introduced by the cherry-picked commit.
当一个特定分支包含我们的活动分支需要的某个提交时,我们对那个提交执行
cherry-pick!对一个提交执行cherry-pick时,我们会在活动分支上创建一个新的提交,其中包含由拣选出来的提交所引入的修改.
Say that commit 76d12 on the dev branch added a change to the index.js file that we want in our master branch. We don’t want the entire we just care about this one single commit!
假设 dev 分支上的提交
76d12为index.js文件添加了一项修改,而我们希望将其整合到master分支中.我们并不想要整个dev分支,而只需要这个提交!
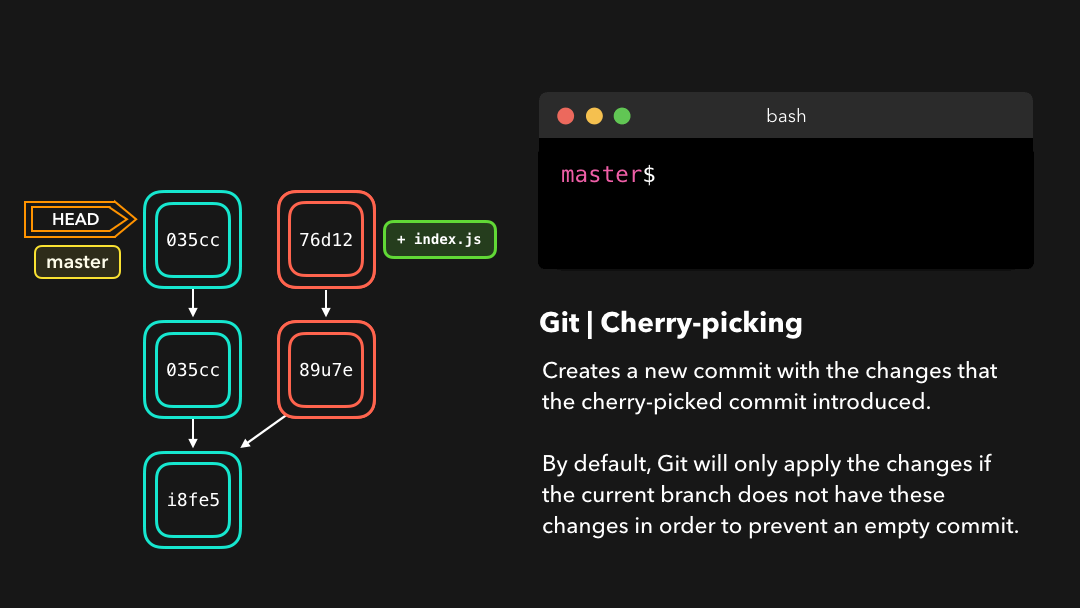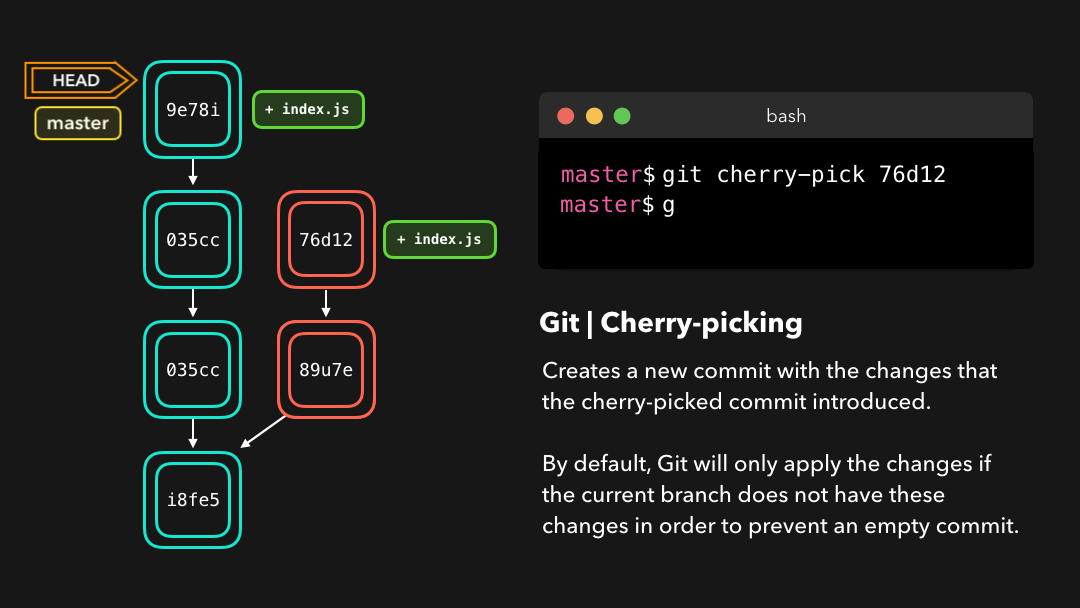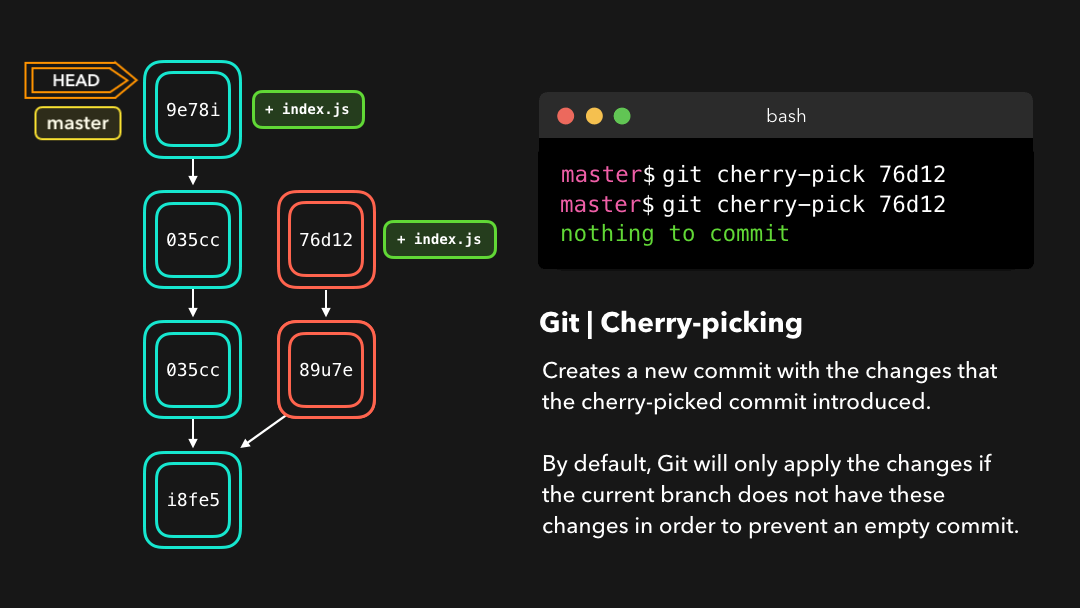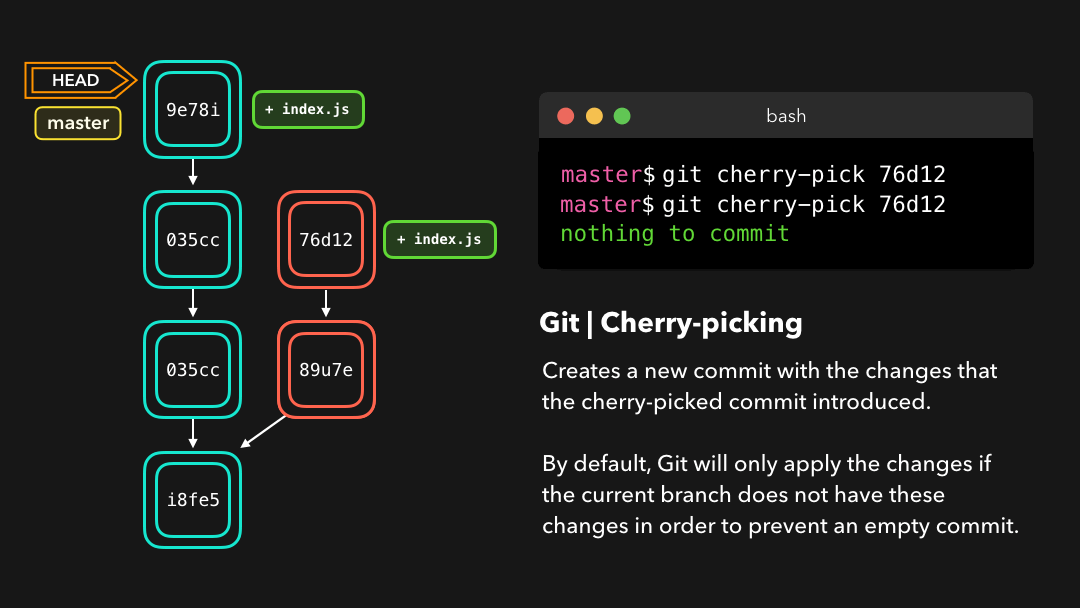
Cool, the master branch now contains the changes that 76d12 introduced!
现在 master 分支包含
76d12引入的修改了.
Fetching
If we have a remote Git branch, for example a branch on Github, it can happen that the remote branch has commits that the current branch doesn’t have! Maybe another branch got merged, your colleague pushed a quick fix, and so on.
如果你有一个远程 Git 分支,比如在 GitHub 上的分支,当远程分支上包含当前分支没有的提交时,可以使用取回.比如当合并了另一个分支或你的同事推送了一个快速修复时.
We can get these changes locally, by performing a git fetch on the remote branch! It doesn’t affect your local branch in any way: a fetch simply downloads new data.
通过在这个远程分支上执行
git fetch,我们就可在本地获取这些修改.这不会以任何方式影响你的本地分支:fetch只是单纯地下载新的数据而已.
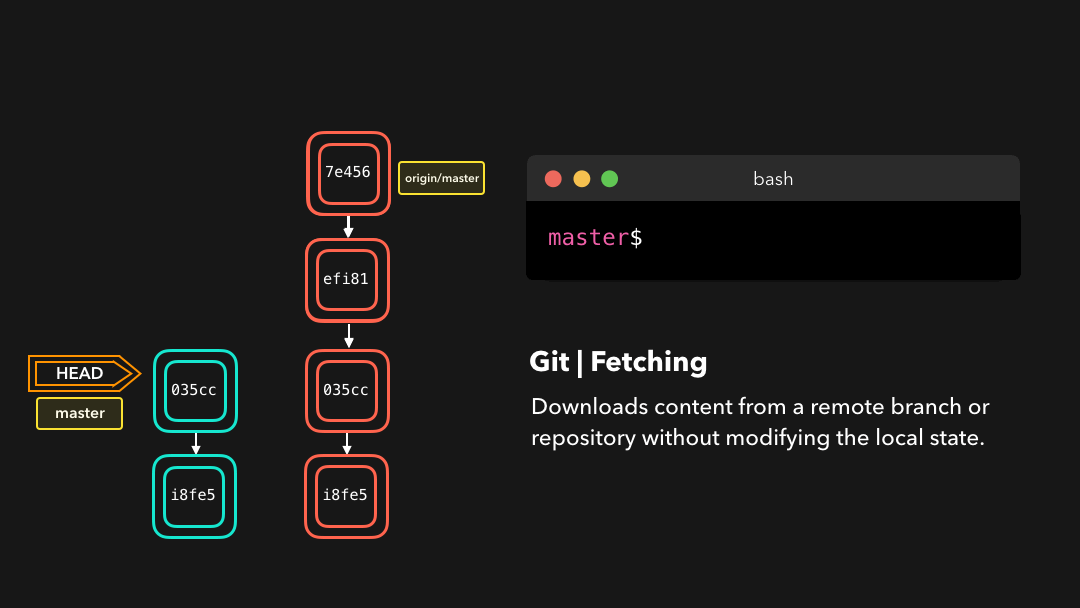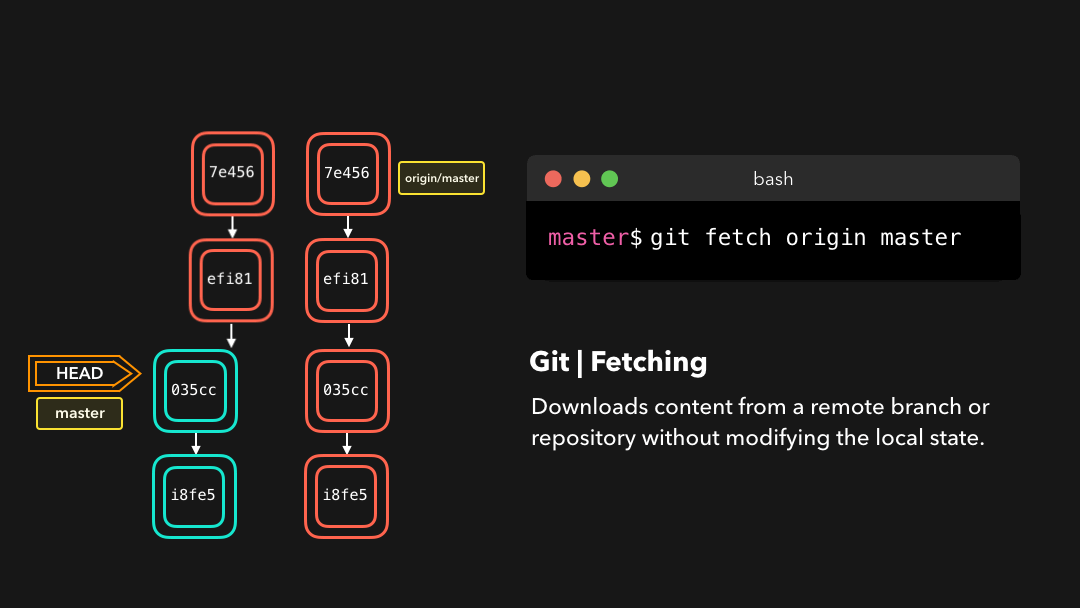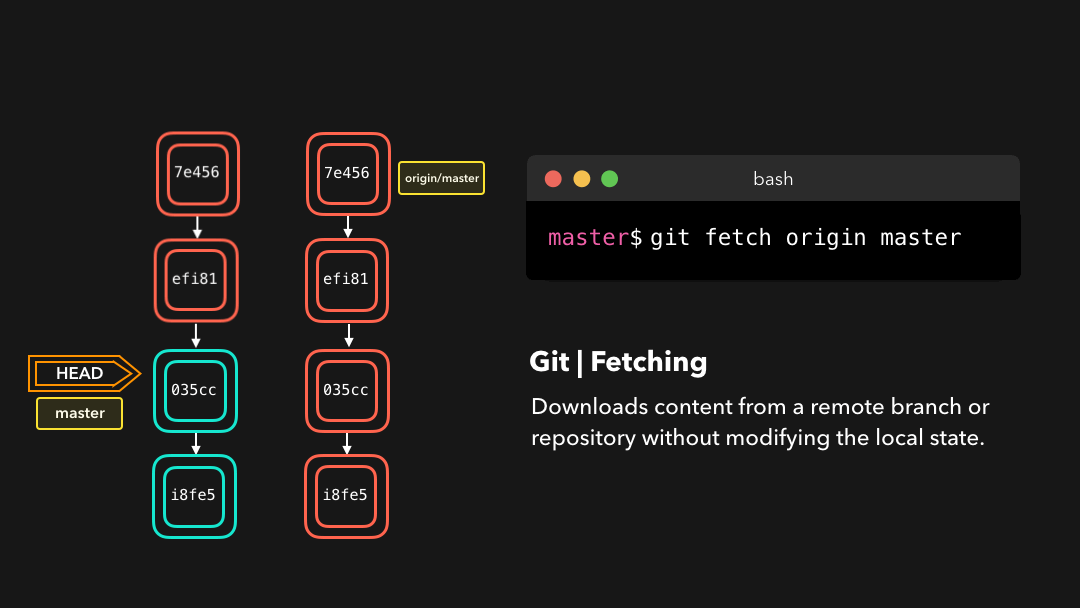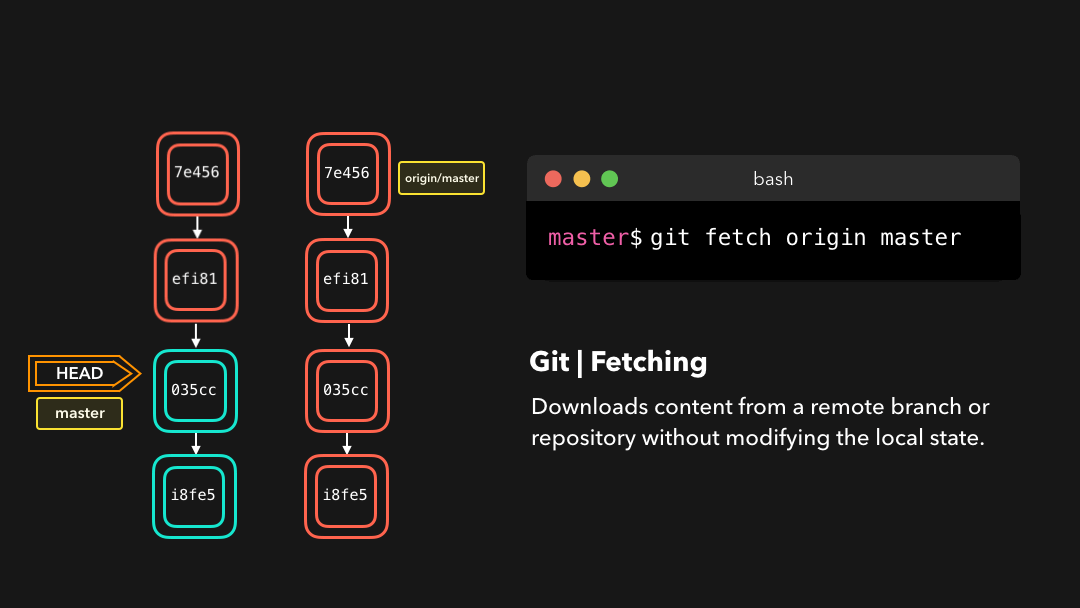
We can now see all the changes that have been made since we last pushed! We can decide what we want to do with the new data now that we have it locally.
现在我们可以看到自上次推送以来的所有修改了.这些新数据也已经在本地了,我们可以决定用这些新数据做什么了.
Pulling
Although a git fetch is very useful in order to get the remote information of a branch, we can also perform a git pull. A git pull is actually two commands in one: a git fetch, and a git merge. When we’re pulling changes from the origin, we’re first fetching all the data like we did with a git fetch, after which the latest changes are automatically merged into the local branch.
尽管
git fetch可用于获取某个分支的远程信息,但我们也可以执行git pull.git pull实际上是两个命令合成了一个:git fetch和git merge.当我们从来源拉取修改时,我们首先是像git fetch那样取回所有数据,然后最新的修改会自动合并到本地分支中.
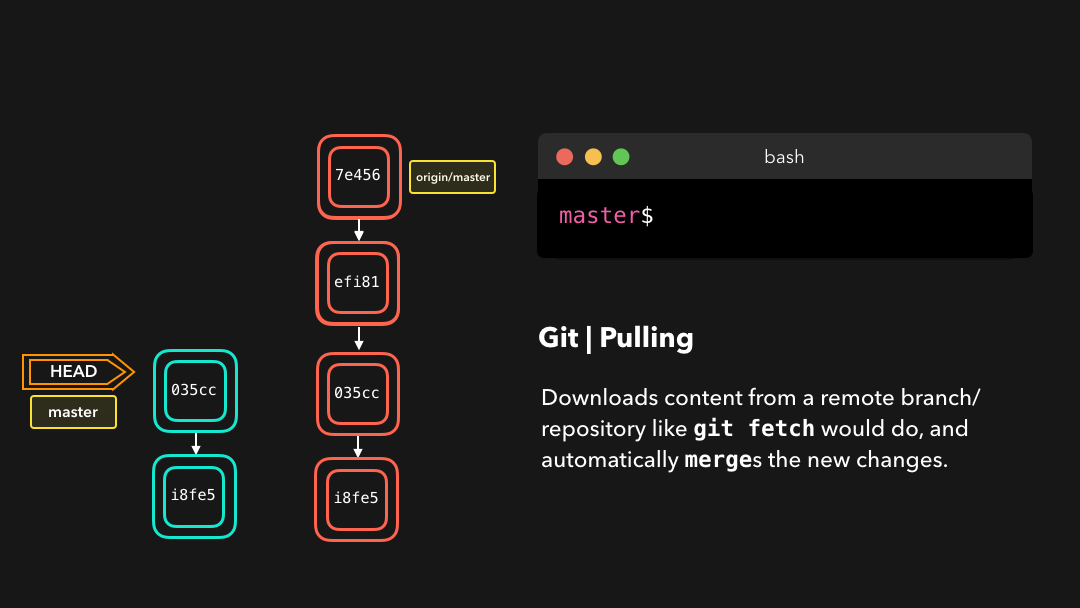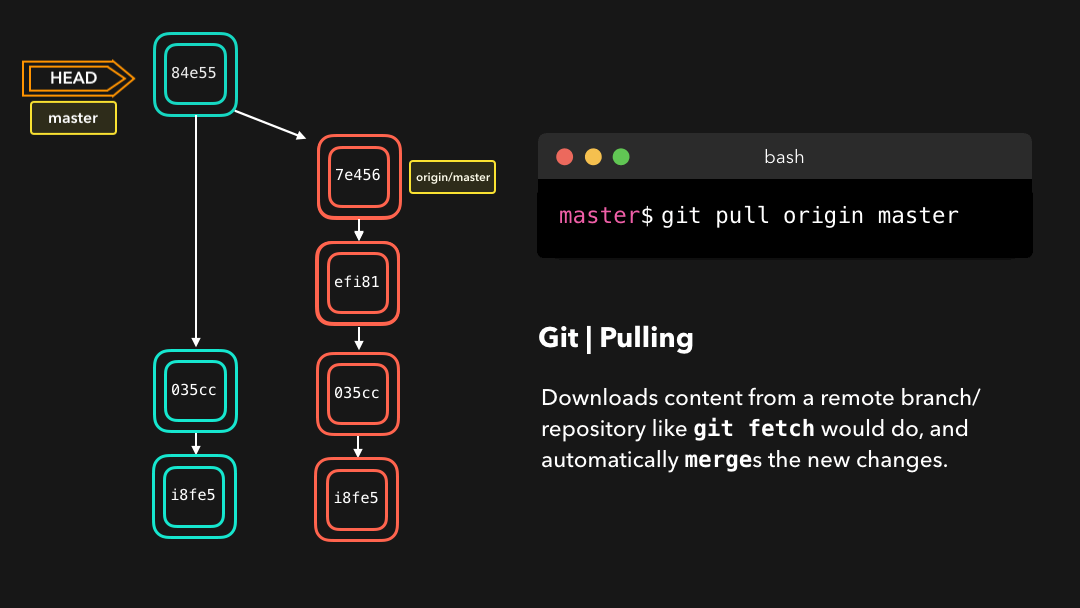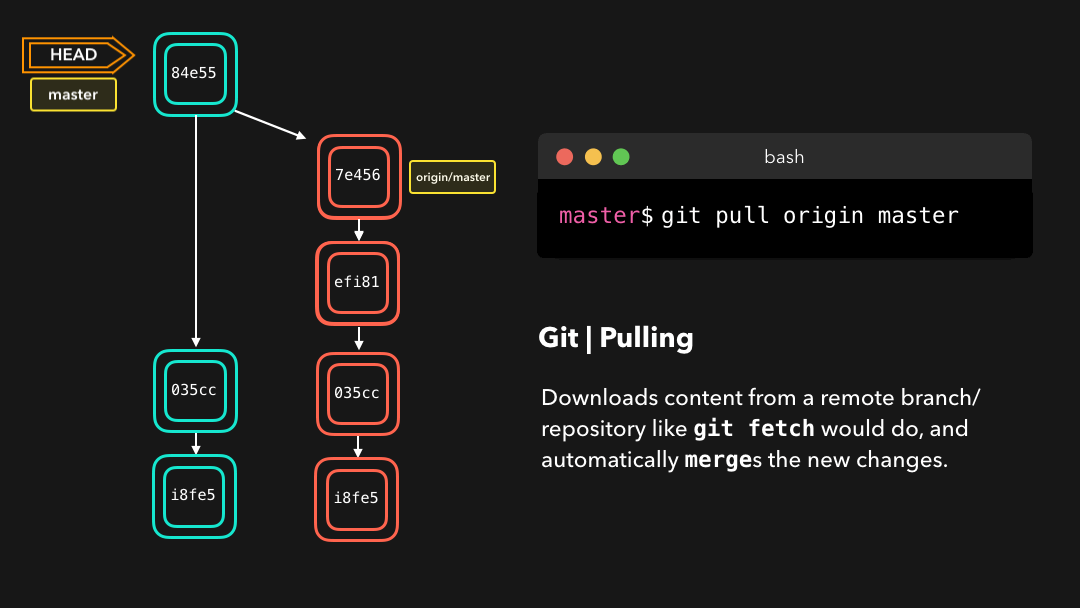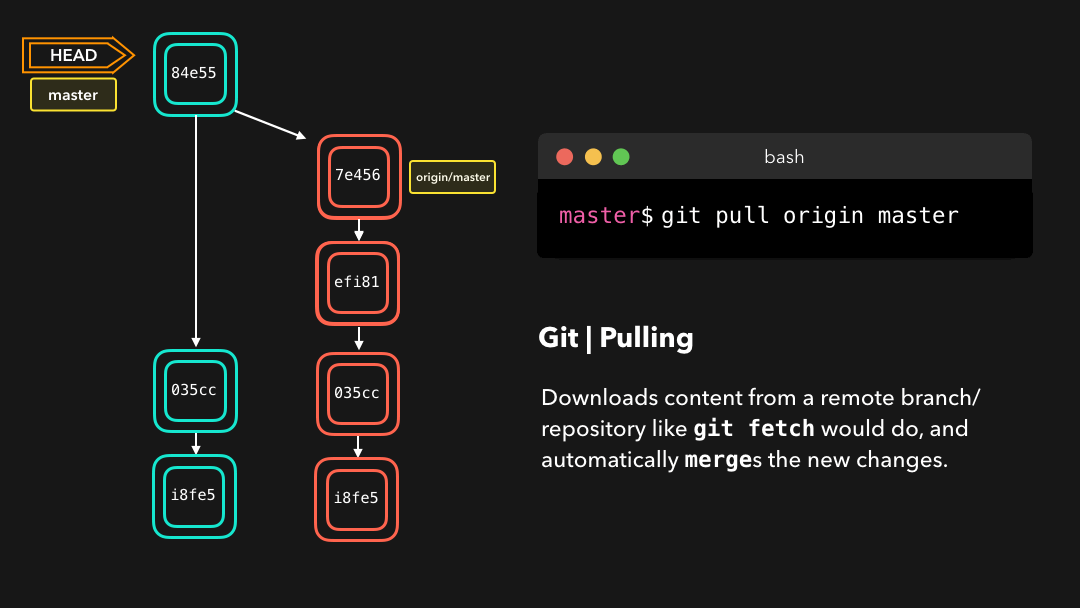
Awesome, we’re now perfectly in sync with the remote branch and have all the latest changes! 🤩
很好,我们现在与远程分支完美同步了,并且也有了所有最新的修改!
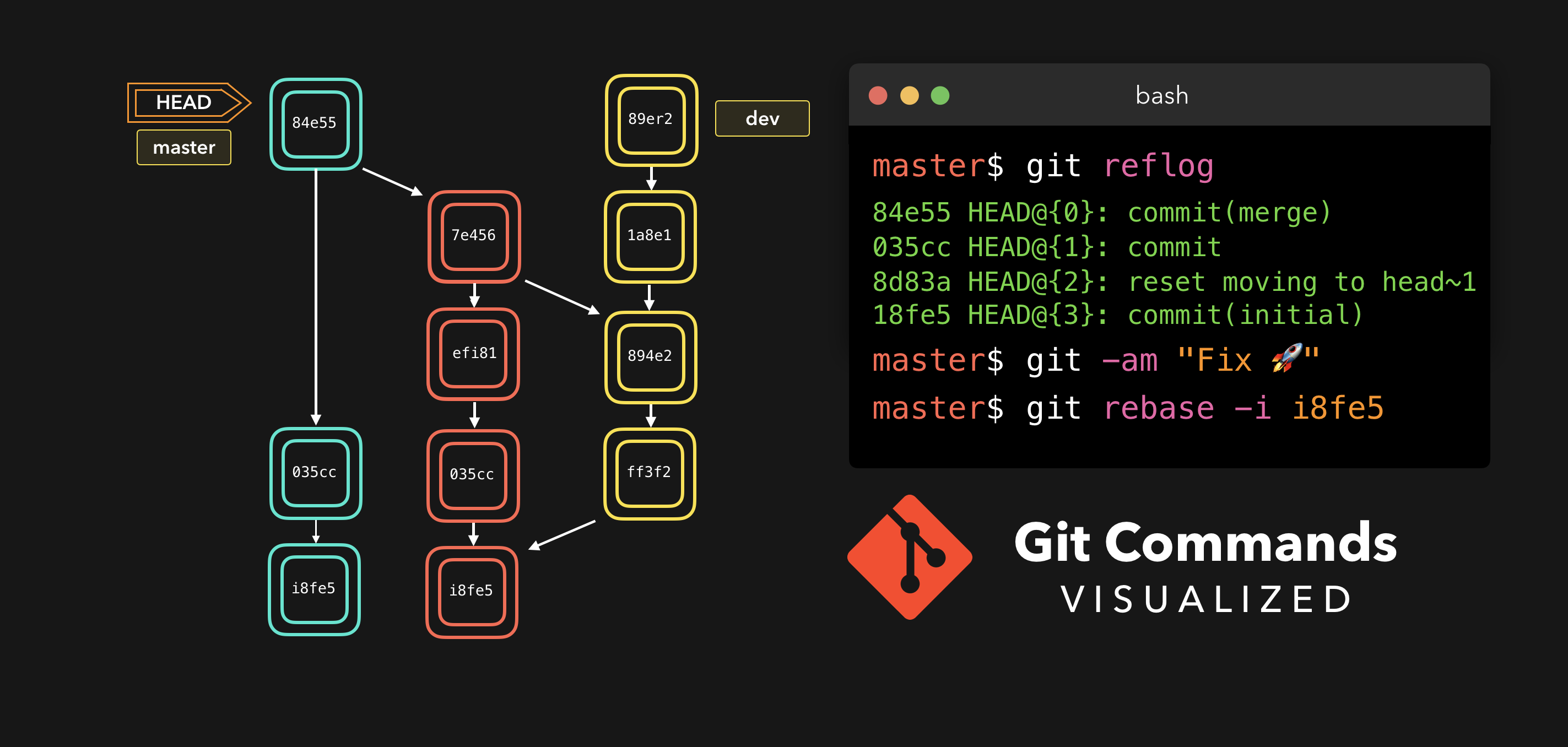
Reflog
Everyone makes mistakes, and that’s totally okay! Sometimes it may feel like you’ve screwed up your git repo so badly that you just want to delete it entirely.
每个人都会犯错,但犯错其实没啥!有时候你可能感觉你把 git repo 完全搞坏了,让你想完全删了了事.
git reflog is a very useful command in order to show a log of all the actions that have been taken! This includes merges, resets, reverts: basically any alteration to your branch.
git reflog是一个非常有用的命令,可以展示已经执行过的所有动作的日志.包括合并、重置、还原,基本上包含你对你的分支所做的任何修改.
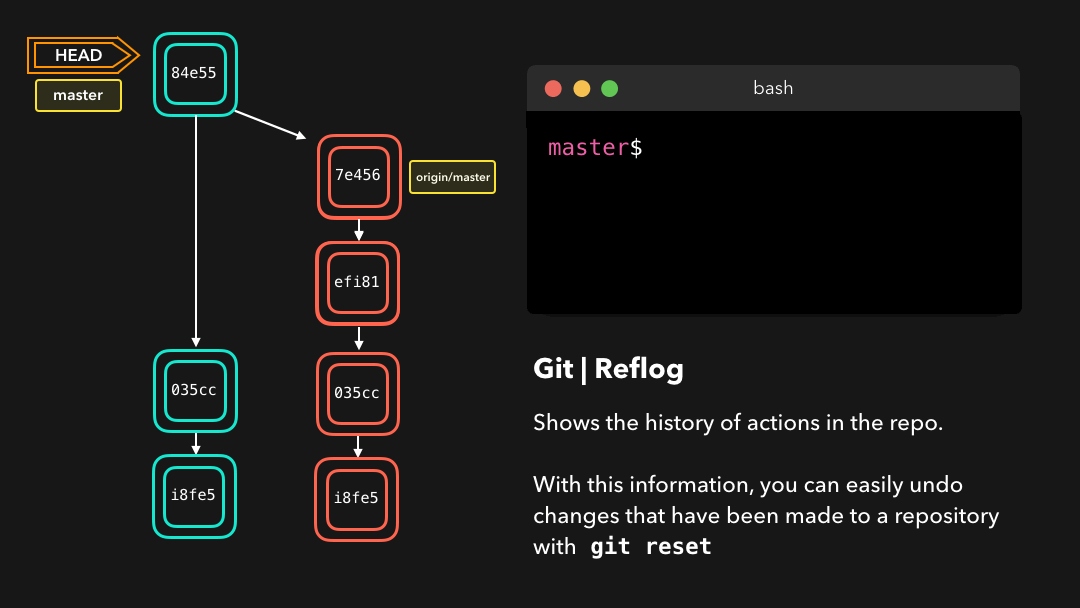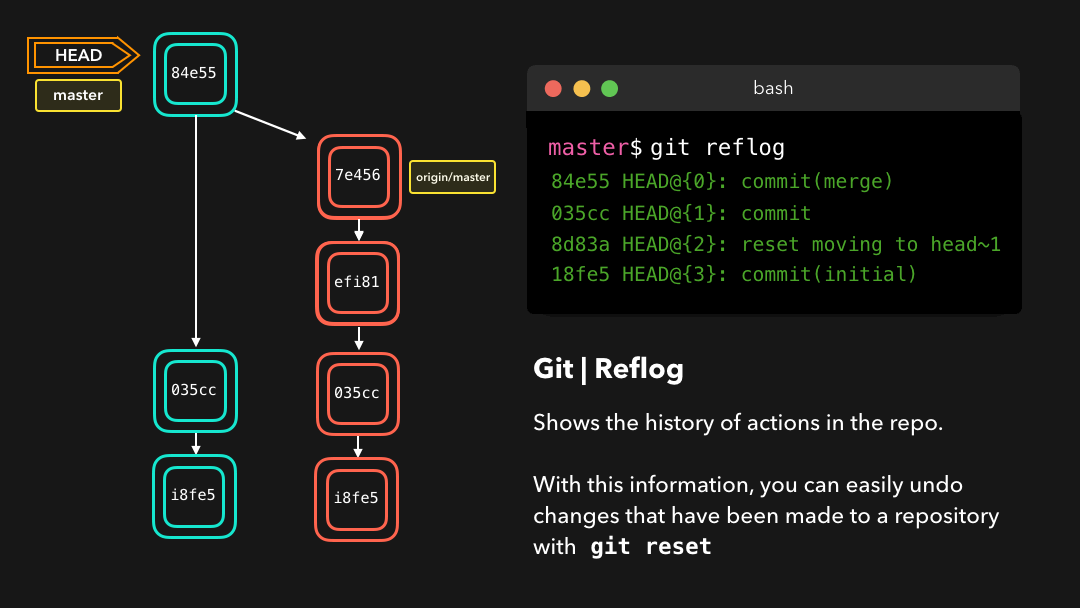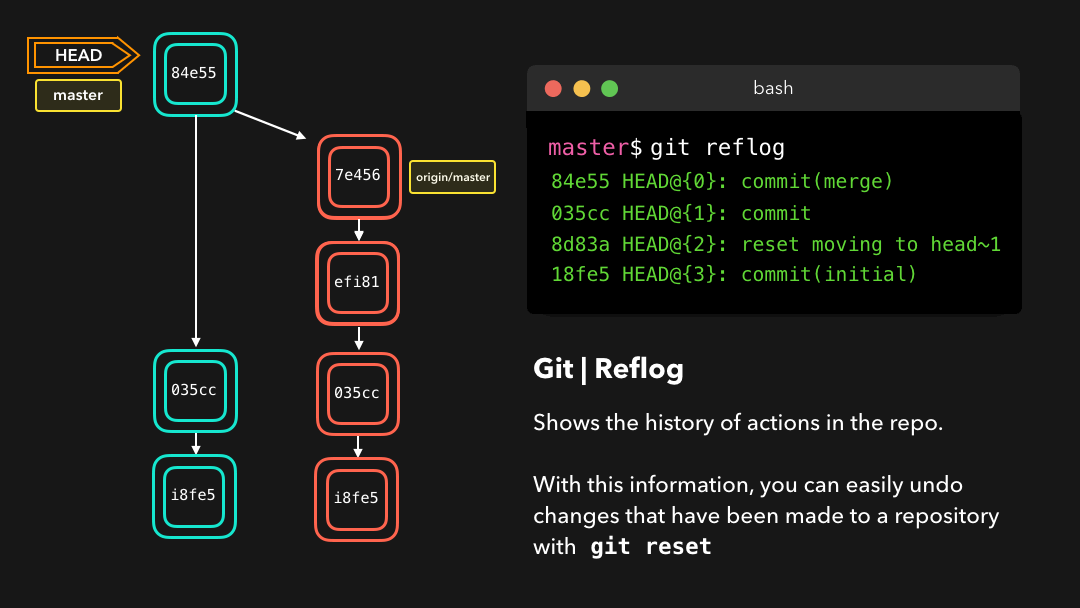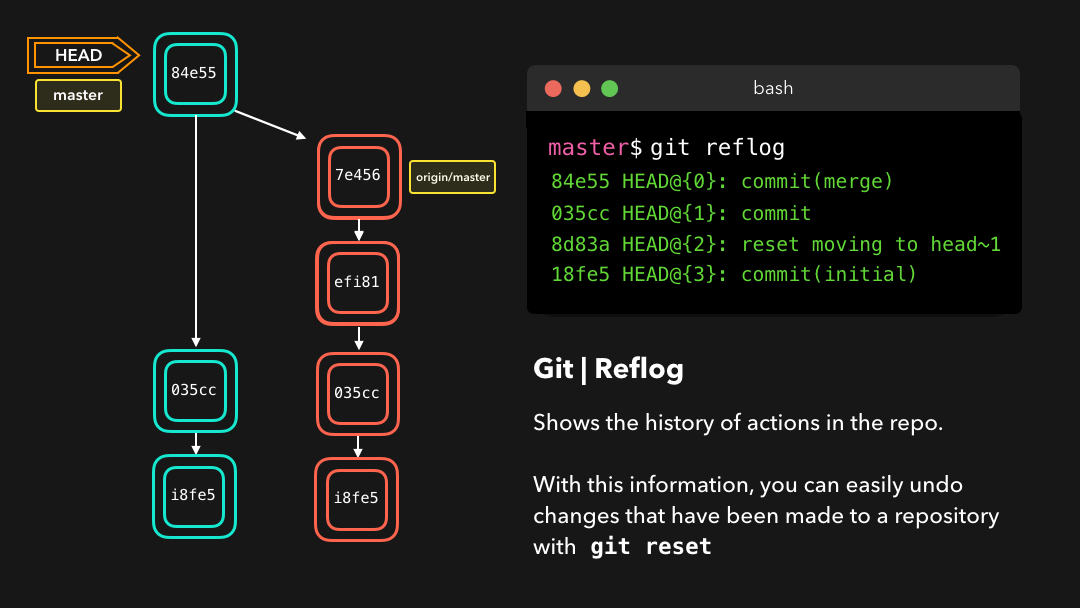
If you made a mistake, you can easily redo this by resetting HEAD based on the information that reflog gives us!
如果你犯了错,你可以根据
reflog提供的信息通过重置HEAD来轻松地重做!
Say that we actually didn’t want to merge the origin branch. When we execute the git reflog command, we see that the state of the repo before the merge is at HEAD@{1}. Let’s perform a git reset to point HEAD back to where it was on HEAD@{1}!
假设我们实际上并不需要合并原有分支.当我们执行
git reflog命令时,我们可以看到这个 repo 的状态在合并前位于HEAD@{1}.那我们就执行一次git reset,将 HEAD 重新指向在HEAD@{1}的位置.
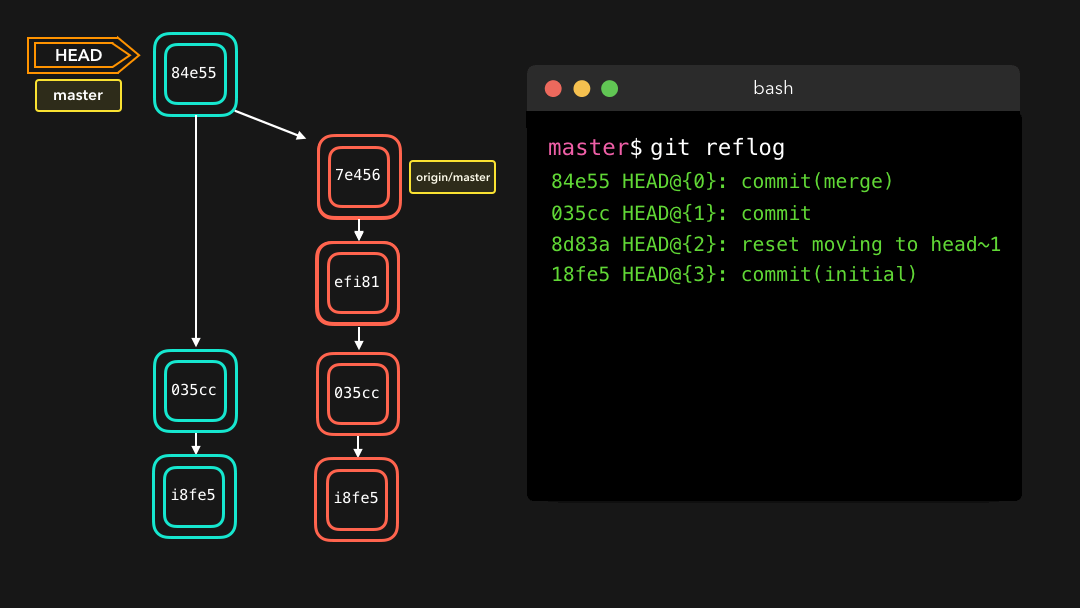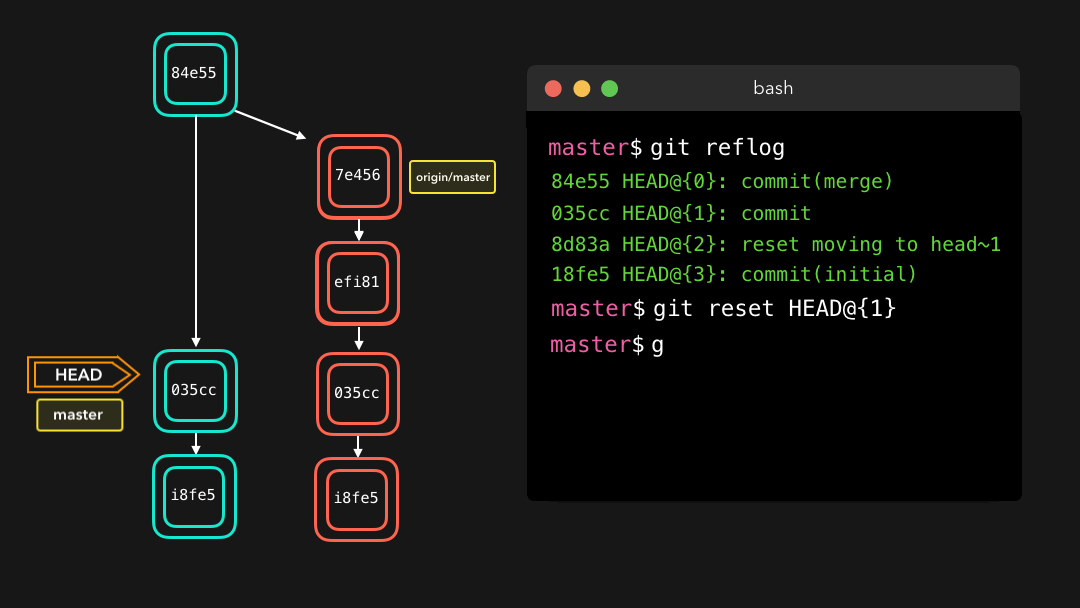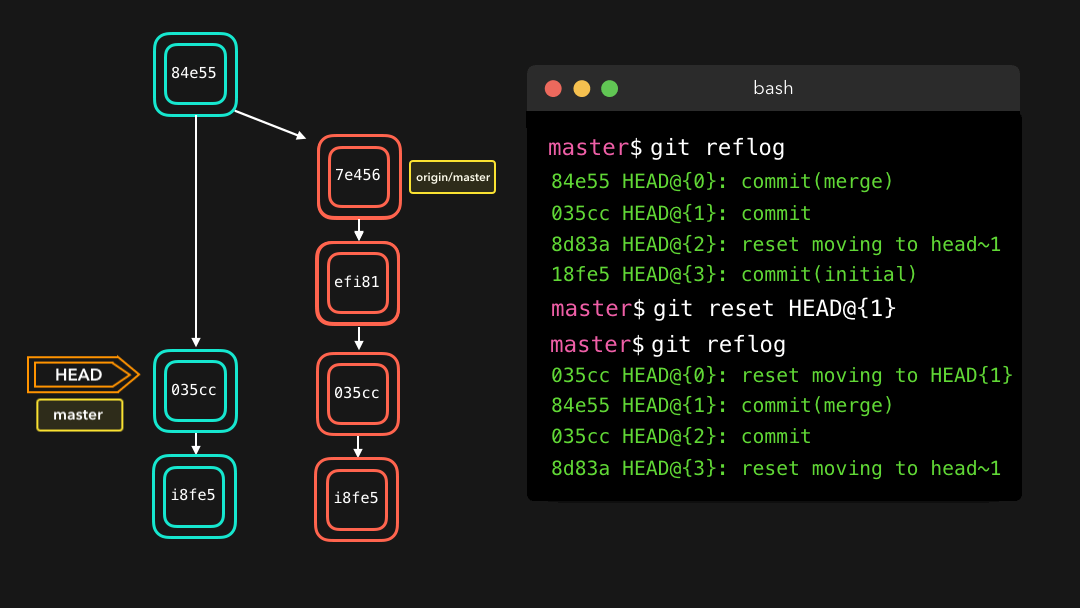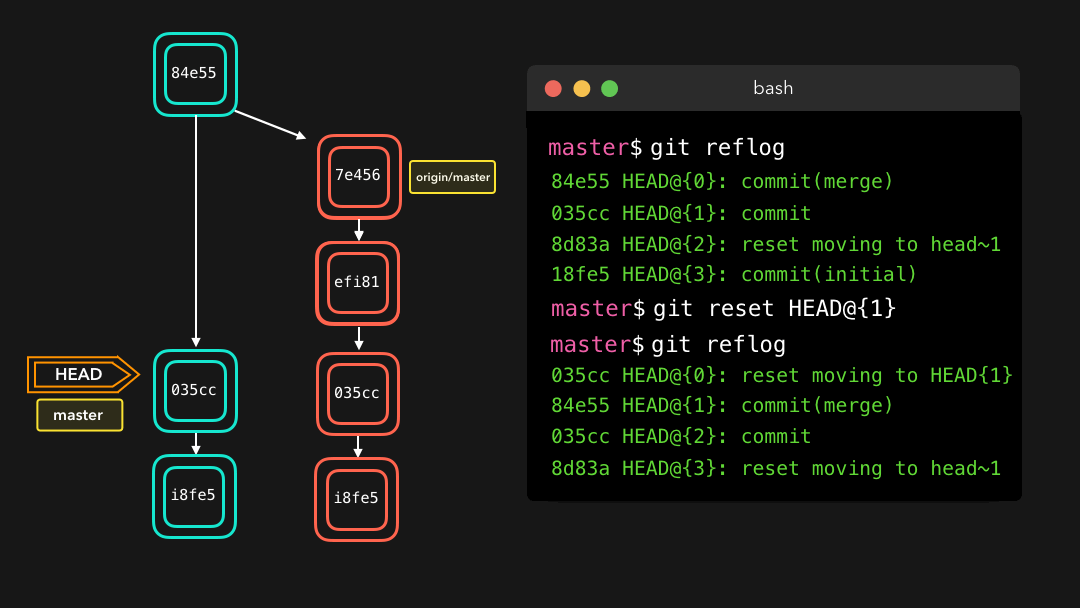
We can see that the latest action has been pushed to the reflog!
我们可以看到最新的动作已被推送给
reflog.
Git has so many useful porcelain and plumbing commands, I wish I could cover them all! 😄 I know there are many other commands or alterations that I didn’t have time for to cover right now - let me know what your favorite/most useful commands are, and I may cover them in another post!
And as always, feel free to reach out to me! 😊



